The members of family Aereidae, generally referred to as herons, are freshwater and coastal wading birds. They have a long bill which is used for catching aquatic prey. Depending on their appearance and behavior, the family members are termed herons, egrets, or bitterns. Herons and egrets can be considered synonyms as they are not biologically distinct. Generally a egret is white, while species referred to as a heron are usually not predominantly white. Bitterns tend to be smaller than herons and more difficult to spot because they favor reed habitats.
The smallest of the family, the dwarf bitten, is 25–30 cm (9.8–11.8 in) in length. The largest, the goliath heron, is 150 cm tail (5 ft). Heron necks can retract in an s-shape so depending on whether or not the neck is extend they can look very different. Unlike most birds with long necks, the neck is usually retracted in flight. Their legs are long and their feet are big. There are 3 forward pointing toes and one backward.
Herons are found on all continents except Antarctica. Most species migrate and when they do it is usually at night. They are mainly found in temperate or tropic regions near water. The male usually initiates nest building and is usually joined later by the slected female. Nest are built mainly in trees or on the ground, but bitterns always locate theirs on the ground. A typical hunting behavior is to stand in the water patiently staring to sight an unsuspecting fish, the neck curved into its s-shape, then rapidly uncurling to spear the prey with its bill. In addition to aquatic prey, some species eat rodents, bird eggs, and even other birds.
Taxonomy
There are 17 genera. Many of the herons are in Ardea, but some in this genus are termed egrets. In Egreta most species are called egrets, although some are known as herons. Pond herons are in Ardeola and Ixobrychus, bitters in Botaurus, night-herons in Gorsachius and Nycticorax.
Etymology
The name comes from the latin ardea for heron.
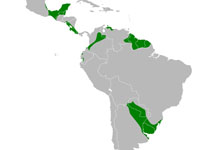
Genus Agamia - 1 species
Heron,_Agami Agamia agami
Description: Bluish upperparts; light chestnut neck, underparts; white line down center of foreneck; yellowish bill, legs . Short legs for a heron. Thin bill is longer than head. Length: 66–76 centimetres (26–30 in).
Distribution: Mexico through Central America to Peru and Chile.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in freshwater environments including wetlands. Usually located below 300 m (1000 ft). Colonial nest sites located over water in either rushes or trees.
Status: Vulnerable.
Image by: 1) Gossip Guy 2) Daniel Hinkley - Panama 3) Jerry Oldenettel - Belize 4) David Rodríguez Arias - Costa RicaDistribution: Mexico through Central America to Peru and Chile.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in freshwater environments including wetlands. Usually located below 300 m (1000 ft). Colonial nest sites located over water in either rushes or trees.
Status: Vulnerable.
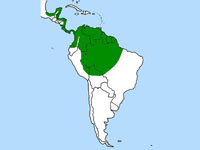



Genus Ardea
Ardeais the signature genus of the Ardeidae family. Most of the twelve species in the genus are called herons, but some are termed egrets. They are the largest members of the family. These are powerful tall birds with large spear-like bills, long necks and long legs, which usually hunt by waiting motionless or stalking their prey in shallow water before seizing it with a sudden lunge. While flying their large wings beat slowly producing a steady flight. Most breed colonially in trees, building large nests with sticks.
Egret,_Great also Great White Egret Ardea alba
Description: White plumage; yellow bill; black legs, feet. Differentiated from white morph of great blue heron by its black legs. Distinguish snowy egret from juvenile great white egret by snow’s yellow feet. Length: 80 to 104 cm (31 – 41 in), wingspan 131 – 170 cm (52 – 67 in), weight 700 to 1,500 g (1.5 – 3.3 lb).
Distribution: Found in temperate and tropical regions on all continents, except Antarctica.
Habitat and Behavior: Temperate or tropic regions near fresh water, but also occasionally ocean beaches. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended. Slow wing beats when flying.
Subspecies:
A. a. alba – Europe
A. a. egretta – Americas
A. a. melanorhynchos – Africa
A. a. modesta – India, southeast Asia, Australasia. Note: smallest subspecies modesta also considered species eastern great egret.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Great Egret is much bigger and has a proportionally longer neck.
Similar to: Great Blue Heron. White morph of Great Blue Heron has gray legs; Great Egret has black legs. Great Blue Heron has thicker neck and thicker bill.
Similar to: Intermediate Egret. Great Egret is larger than Intermediate Egret. Great Egret has a proportionally longer neck. The top of the longer bill of Great Egret nearly aligns with the top of its head; the top of Intermediate Egret's bill is lower relative to the top of its head.
Similar to: Little Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Little Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Snowy Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2, 5, 6, 10) Dick Daniels - New Jersey, Australia 3) Jack Wolf - California
4) Tony Dudley - Australia 6) Ted Grussing 8 Cristiano Crolle - Ticino River, Italy 9) Sandy Cole - Flamingo Gardens in Florida 11) Dick - St. Thomas 12) Dan Langer - Rye, New Hampshire 13) Video by Avibirds. More vidoesDistribution: Found in temperate and tropical regions on all continents, except Antarctica.
Habitat and Behavior: Temperate or tropic regions near fresh water, but also occasionally ocean beaches. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended. Slow wing beats when flying.
Subspecies:
A. a. alba – Europe
A. a. egretta – Americas
A. a. melanorhynchos – Africa
A. a. modesta – India, southeast Asia, Australasia. Note: smallest subspecies modesta also considered species eastern great egret.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Great Egret is much bigger and has a proportionally longer neck.
Similar to: Great Blue Heron. White morph of Great Blue Heron has gray legs; Great Egret has black legs. Great Blue Heron has thicker neck and thicker bill.
Similar to: Intermediate Egret. Great Egret is larger than Intermediate Egret. Great Egret has a proportionally longer neck. The top of the longer bill of Great Egret nearly aligns with the top of its head; the top of Intermediate Egret's bill is lower relative to the top of its head.
Similar to: Little Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Little Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Snowy Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
2) Juvenile, adult 3 - 8) nonbreeding 9 - 12) Breeding












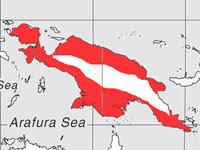
Egret,_Intermediate also Yellow-billed Egret Ardea intermedia
Description: Intermediate in size between great white egret and other smaller egrets. White plumage; dark legs; relatively thick yellow bill.
Distribution: Africa, India, southeast Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Usually stalks upright with neck extended forward.
Subspecies:
A. i. brachyrhyncha – subSaharan Africa
A.i. intermedia – eastern Asia, India
A. i. plumifera – easterb Indonesia, Australasia Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is larger than Intermediate Egret. Great Egret has a proportionally longer neck. The top of the longer bill of Great Egret nearly aligns with the top of its head; the top of Intermediate Egret's bill is lower relative to the top of its head.
Image by: 1) Lin_Sun_Fong - Taiwan 2) J M Garg - India 3) Alpsdake - Japan 4) Lip Kee Yap - AustraliaDistribution: Africa, India, southeast Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Usually stalks upright with neck extended forward.
Subspecies:
A. i. brachyrhyncha – subSaharan Africa
A.i. intermedia – eastern Asia, India
A. i. plumifera – easterb Indonesia, Australasia Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is larger than Intermediate Egret. Great Egret has a proportionally longer neck. The top of the longer bill of Great Egret nearly aligns with the top of its head; the top of Intermediate Egret's bill is lower relative to the top of its head.




Heron,_Black-headed Ardea melanocephala
Description: Dark grey upperparts; paler underparts; white throat, underwings.
Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa, Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in plains and also near water. Eats insects, eggs, small birds. Colonial nests in trees, reed beds, or cliffs. Most do not migrate, but some in rainy season.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Arno Meintjes 2) Dick Daniels - Nairobi National Park, Kenya 3) Dick - Masai Mara, kenya
4) Craig Adam - South Africa 5) Dick Daniels - South Africa 6) Dick - Tanzania 7) Dick - TanzaniaDistribution: Sub-Saharan Africa, Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in plains and also near water. Eats insects, eggs, small birds. Colonial nests in trees, reed beds, or cliffs. Most do not migrate, but some in rainy season.
Status: Least concern.







Heron,_Cocoi Ardea cocoi
Description: Grey upperparts, upper-wings; mainly white neck with thin black steaks; black cap extends below the eyes. Length 95 to 130 cm (37.5–51 in), weight 1.14 – 3.2 kg (2.5 to 7 lb), wing length 42 to 45 cm (16.5–18 in), tail length 16 to 17 cm (6.5–7 in),
Distribution: Panama and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers wet areas that have wading areas. Migrates if breeding area get cold. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended. Feeds mainly on fish; also crabs, amphibians, and crustaceans. Roosts in trees overlooking water.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 2) Cláudio
Timm - Brazil 3) Nori Almaeda 4) Dario
Niz 5) Gustavo_Duran - ArgentinaDistribution: Panama and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers wet areas that have wading areas. Migrates if breeding area get cold. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended. Feeds mainly on fish; also crabs, amphibians, and crustaceans. Roosts in trees overlooking water.
Status: Least concern.





Heron,_Goliath Ardea goliath
Description: Largest heron. Grey back, upper-wings; pale chestnut under-wings; white chin, throat, fore-neck, upper breast; chestnut head, crest, face, back and sides of neck; black streaks along the fore-neck; buffy lower breast, belly. Height 120 to 152 cm (3 ft 11 in–5 ft), wingspan 185 to 230 cm (6 ft 1 in–7 ft 7 in), weight 4 to 5 kg (8.8–11 lb).
Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers to be around water, even while flying. Voice, a deep bark, heard up to 2 km. Feeds like other Ardea herons, but can wade deeper because of size.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Gray Heron has white neck; Goliath Heron has chestnut back and sides of neck.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Goliath Heron is substantially larger and has more pronounced black stripes on neck than Purple Heron.
Image by: 1) Arno Meintjes 2, 3, 4, 5) Dick Daniels - St. Lucia, South Africa 6) Sandy Cole - St. Lucia, South Africa 7)
Dick - St. Lucia, South Africa 8) Dick - the Jacksonville Zoo in Florida 9) Dick - San
Diego ZooDistribution: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers to be around water, even while flying. Voice, a deep bark, heard up to 2 km. Feeds like other Ardea herons, but can wade deeper because of size.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Gray Heron has white neck; Goliath Heron has chestnut back and sides of neck.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Goliath Heron is substantially larger and has more pronounced black stripes on neck than Purple Heron.
1) Breeding









Heron,_ Gray Ardea cinerea
Description: Grey upperparts; greyish-white underparts; white head with black supercilium; pinkish-yellow bill; yellow eyes; long yellowish-brown legs.
Distribution: Europe, Asia, Afica.
Habitat and Behavior: Temperate or tropic regions near fresh water, but also occasionally ocean beaches. Migrates if breeding locals get cold. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended.
Subspecies:
A. c. cinerea – Europe, western Asia, subsaharan Africa A. c. firasa – Madagascar A. c. jouyi – eastern Asia
A. c. monicae – Mauritania Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Blue Heron. Ranges do not overlap.
Similar to: Goliath Heron. Gray Heron has white neck; Goliath Heron has chestnut back and sides of neck.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Purple Heron has stripe on side of neck. Gray Heron has white neck.
Image by: 1, 2) Arno Meintjes 3)
Dick Daniels- Scotland 4) Cristiano Crolle - Manzolino, Italy 5) Dick - South Africa 6) Dick - Nepal Distribution: Europe, Asia, Afica.
Habitat and Behavior: Temperate or tropic regions near fresh water, but also occasionally ocean beaches. Migrates if breeding locals get cold. Flies with neck retracted, walks with it extended.
Subspecies:
A. c. cinerea – Europe, western Asia, subsaharan Africa A. c. firasa – Madagascar A. c. jouyi – eastern Asia
A. c. monicae – Mauritania Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Blue Heron. Ranges do not overlap.
Similar to: Goliath Heron. Gray Heron has white neck; Goliath Heron has chestnut back and sides of neck.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Purple Heron has stripe on side of neck. Gray Heron has white neck.






Heron,_Great-billed Ardea sumatrana
Description: Grey upperparts. neck, breast; whitish belly.
Distribution: Southeast Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found at shallow coastal areas, lakes and sometimes small ponds. Feeds in shallow water, spearing fish with its long, sharp bill.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron is larger and darker than Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron has uniformly colored neck; Purple Heron does not.
Image by: 1) Ralph Green - Australia 2, 3) Jerry Oldenettel - AustraliaDistribution: Southeast Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found at shallow coastal areas, lakes and sometimes small ponds. Feeds in shallow water, spearing fish with its long, sharp bill.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron is larger and darker than Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron has uniformly colored neck; Purple Heron does not.



Heron,_Great Blue Ardea herodias
Description: Grey plumage; darker crown; lighter face; grey legs. Leg color of white morph distinguishes from black-legged great white egret. Largest North American heron.
Distribution: North America, Central America, Caribbean, Galapagos.
Habitat and Behavior: Can adapt to almost any wetland habitat in its range. Some winter in freezing climates as long as rivers don’t freeze . Feeds like other Ardea herons, but can wade deeper because of size.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. White morph of Great Blue Heron has gray legs; Great Egret has black legs. Great Blue Heron has thicker neck and thicker bill.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Ranges do not overlap.
Image by: 1) Dick Daniels - Galapagos 2) Andy Jones - Florida 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) Dick - North Carolina 11) Ted Grussing 12) Linda Westerinen - CaliforniaDistribution: North America, Central America, Caribbean, Galapagos.
Habitat and Behavior: Can adapt to almost any wetland habitat in its range. Some winter in freezing climates as long as rivers don’t freeze . Feeds like other Ardea herons, but can wade deeper because of size.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. White morph of Great Blue Heron has gray legs; Great Egret has black legs. Great Blue Heron has thicker neck and thicker bill.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Ranges do not overlap.
1) Juvenile 2) White morph












Heron,_Humblot's Ardea humbloti
Description: Mainly dark grey plumage; black crown; pale yellowish bill; greyish legs.
Distribution: Most common to north and west coasts of Madagascar. Also found Comoro Islands and Mayotte
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers coastal areas, also visits freshwater lakes. Nests in trees, but also on ground. Feeds on fish, eels, crusteations.
Status: Endangered. Threatened by poaching and habitat disruption.
Image by: 1) David Cook - Madagascar 2) Daniel Vaulot - Madagascar 3) Ross Tsai - Madagascar 4) Amy_McAndrewsDistribution: Most common to north and west coasts of Madagascar. Also found Comoro Islands and Mayotte
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers coastal areas, also visits freshwater lakes. Nests in trees, but also on ground. Feeds on fish, eels, crusteations.
Status: Endangered. Threatened by poaching and habitat disruption.
1) Juvenile




Heron,_Purple Ardea purpurea
Description: Purple wings; purplish neck with stripe on sides; grey back; yellow narrow bill. Length 78-97 cm (31–38 in), height from 70 to 94 cm (28 to 37 in), wingspan 120–152 cm (47–60 in), weight. 0.5 to 1.35 kg (1.1 to 3.0 lb).
Distribution: Europe, Asia, Africa, Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Favors densely vegetated habitats near water, especially reed beds. Eats fish, rodents, frogs and insects. Hunts by stalking or waiting in ambush. Nesting colonies usually in reed beds.
Subspecies:
A. p. purpurea – Europe, Africa
A. p. bournei – Cape Verde Islands
A. p. madagascariensis – Madagascar
A. p. manilensis – Asia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Purple Heron has stripe on side of neck. Gray Heron has white neck.
Similar to: Goliath Heron. Goliath Heron is substantially larger and has more pronounced black stripes on neck than Purple Heron.
Similar to: Great-billed Heron. Great-billed Heron is larger and darker than Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron has uniformly colored neck; Purple Heron does not.
Image by: 1) Shankar S - Kenya 2) Dick Daniels - South Africa 3) Sandy Cole - St. Lucia 4) Steve Garvie - Kenya 5) Koshy_Koshy 6) Cristiano Crolle - Italy 7) Imran_Shah - Pakistan 8) Shrikant_Rao in IndiaDistribution: Europe, Asia, Africa, Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Favors densely vegetated habitats near water, especially reed beds. Eats fish, rodents, frogs and insects. Hunts by stalking or waiting in ambush. Nesting colonies usually in reed beds.
Subspecies:
A. p. purpurea – Europe, Africa
A. p. bournei – Cape Verde Islands
A. p. madagascariensis – Madagascar
A. p. manilensis – Asia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Gray Heron. Purple Heron has stripe on side of neck. Gray Heron has white neck.
Similar to: Goliath Heron. Goliath Heron is substantially larger and has more pronounced black stripes on neck than Purple Heron.
Similar to: Great-billed Heron. Great-billed Heron is larger and darker than Purple Heron. Great-billed Heron has uniformly colored neck; Purple Heron does not.








Heron,_White-bellied Ardea insignis
Description: Grey upperparts; relatively long neck; greyish-white neck plume; black bill greenish at base and tip; white chin and central parts of underparts; blackish legs. Second largest heron.
Distribution: eastern Himalayas.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands of tropical and subtropical forests.
Status: Critically endangered.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) Mahesh Lyer - Bhutan 3) Dr. Raju KasambeDistribution: eastern Himalayas.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands of tropical and subtropical forests.
Status: Critically endangered.
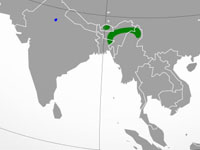


Heron,_White-necked also Pacific Heron Ardea pacifica
Description: Dark grey upperparts; white head, underparts; white neck with large black white spots on throat; black bill, legs, feet.
Distribution: Indonesia, New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand.
Habitat and Behavior: Found tidal areas shallow fresh water areas including drainage ditches. Nests high in trees near water.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Dick Daniels - Kuranda Birdworld, Australia 2) birdsaspoetry 3) David_Jenkins 4) Jim Bendon - Indonesia Distribution: Indonesia, New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand.
Habitat and Behavior: Found tidal areas shallow fresh water areas including drainage ditches. Nests high in trees near water.
Status: Least concern.




Genus Ardeola
Pond herons are stocky species with a short neck, short thick bill, typically buff or brownish back, and colored or streaked foreneck and breast. In summer, adults may have long neck feathers. Ardeola herons are transformed in flight, looking very white due to the brilliant white wings. Length 40–50 cm (16–20 in) , wingspan 80–100 cm (31–39 in).
They are often found on ponds and feed on fish, amphibians.and insects. Pond herons breed in wetlands, nesting in trees or shrubs.
Heron,_Chinese Pond Ardeola bacchus
Description: Yellow bill with black tip; yellow legs, eyes. Breeding: blue wings; red head, neck, breast; white belly. Nonbreeding: greyish-brown mixed with white. Nonbreeding plumage of Chinese, Indian, and Javan pond herons virtually indistinguishable.
Distribution: India, east Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in shallow wetlands, fresh or salt. Mainly restricted to lowlands. Eats fish, insects, and crustaceans. Blue-green eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by:1) kclama 2, 3)
Lip Kee
4, 5)
JJ Harrison - ThailandDistribution: India, east Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in shallow wetlands, fresh or salt. Mainly restricted to lowlands. Eats fish, insects, and crustaceans. Blue-green eggs.
Status: Least concern.
1) Breeding





Heron,_Indian Pond Ardeola grayii
Description: Buff brown back; white wings, belly; yellow bill with black tip; yellow eyes. Breeding has darker mantle. Nonbreeding plumage of Chinese, Indian, and Javan pond herons virtually indistinguishable
Distribution: India, southeast Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found near ponds and in marshy wetlands. Eats fish, crustaceans, tadpoles, aquatic insects. Hunts by wading, but occasionally disturb frogs by low flight. Nests mainly in trees, but also small bushes. Males collects nest material which female utilizes.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Kaippally 2, 3)
J M Garg - Kolkata, West Bengal, India 4) Dick Daniels - Jacksonville Zoo in FloridaDistribution: India, southeast Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found near ponds and in marshy wetlands. Eats fish, crustaceans, tadpoles, aquatic insects. Hunts by wading, but occasionally disturb frogs by low flight. Nests mainly in trees, but also small bushes. Males collects nest material which female utilizes.
Status: Least concern.
1) Nonbreeding 2, 3, 4) Breeding




Heron,_Javan Pond Ardeola speciosa
Description: Yellow bill with black tip; yellow eyes, legs. Breeding: orange, slaty, and white plumage. Nonbreeding: brown flecked with white plumage. Nonbreeding plumage of Chinese, Indian, and Javan pond herons virtually indistinguishable.
Distribution: Southeast Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Fresh and saltwater wetlands. Eats insects, fish, crabs.
Subspecies:
A. s. continentalis – Central Thailand to s Indochina
A. s. speciosa – West and central Indonesian Archipelago
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2, 3) Dick Daniels - Tampa's Lowry Park Zoo 4, 6) Dick - Sylvan Heights
5) Sandy Cole - Sylvan HeightsDistribution: Southeast Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Fresh and saltwater wetlands. Eats insects, fish, crabs.
Subspecies:
A. s. continentalis – Central Thailand to s Indochina
A. s. speciosa – West and central Indonesian Archipelago
Status: Least concern.
2, 3) Nonbreeding 4, 5, 6) Breeding
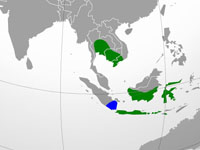





Heron,_Malagasy_Pond- also Madagascar Pond-Heron Ardeola idae
Description: Buff, brown, and black plumage; mainly green bill with black tip; yellow eyes. Breeding adult has more white plumage.
Distribution: Mainly Madagascar. Also Seychelles, and east coast Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found grassy marshes, lakes, ponds, streams, and rice fields. Migrates between Madagascar, where it breeds, and eastern Africa for the warmer seasons.
Status: Endangered due to habitat loss and competition from squacco herons.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) Carol Foil - Rift Valley, Kenya 3) Zak_Pohlen - Madagascar 4) Francesco_Veronesi - KenyaDistribution: Mainly Madagascar. Also Seychelles, and east coast Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found grassy marshes, lakes, ponds, streams, and rice fields. Migrates between Madagascar, where it breeds, and eastern Africa for the warmer seasons.
Status: Endangered due to habitat loss and competition from squacco herons.
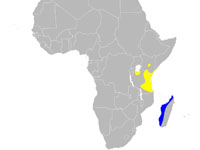



Heron,_Rufous-bellied Ardeola rufiventris f
Description: Dark grey upperparts, head, breast; rufous belly, wings, tail; yellow legs.
Distribution: Central and southern Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found near shallow water along riverbanks and lake shores; also at seasonally flooded wetlands. Nest in trees or shrubs that are normally over water.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) David Schenfeld 2) Lip Kee Yap 3) Steve Garvie - Kenya 4, 5, 6) Ian White - BotswanaDistribution: Central and southern Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found near shallow water along riverbanks and lake shores; also at seasonally flooded wetlands. Nest in trees or shrubs that are normally over water.
Status: Least concern.
1) Juvenile






Heron,_Squacco Ardeola ralloides
Description: Buff brown back; white wings; yellow-grey bill with black tip; yellow eyes.
Distribution: Southern Europe, middle east, winters in Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in permanent or temporary wetland, preferring marshy areas. Eats mainly insect larvae, also fish and frogs. Nests in trees or bushes.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2,5) Dick Daniels - Parc Tsarasaotra (open bird sanctury in Antananrivo, Madagascar 3) Charlie Westerinen - Botswana 4, 7)
Mark S Jobling - Greece 6) Cristiano Crolle - Torrile, ItalyDistribution: Southern Europe, middle east, winters in Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in permanent or temporary wetland, preferring marshy areas. Eats mainly insect larvae, also fish and frogs. Nests in trees or bushes.
Status: Least concern.
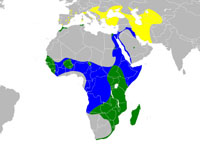






Genus Botaurus
The four Botaurus bitterns are all large chunky, heavily streaked brown birds which breed in large reedbeds. Almost uniquely for predatory birds, the female rears the young alone. They are secretive and well-camouflaged, and despite their size they can be difficult to observe except for occasional flight views.
Bittern, American Botaurus lentiginosus
Description: Mainly brown plumage; buff supercillium; streaked brown and white breast; white throat. Length 58–85 cm (23–33 in), wingspan 92–115 cm (36–45 in), weight 370–1,070 g (0.816–2.36 lb).
Distribution: Breeds in Canada and northern USA; winters southern USA, Central America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in heavily vegetated wet area where they can utilize their camouflage. Walks stealthy stalking its prey or waits in ambush. Solitary nest built close to ground located in coarse vegetation.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron (juvenile), Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; American Bittern has dark bill.
Similar to: Green Heron. Green Heron has green on it; American Bittern is brown with white stripes.
Similar to: Least Bittern. American Bittern much larger than Least Bittern. Least Bittern has dark cap; American Bittern does not.
Image by: 1) H Barrison - Washington 2) Alan D. Wilson - British Columbia 3) Andrea Westmoreland - Florida Distribution: Breeds in Canada and northern USA; winters southern USA, Central America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in heavily vegetated wet area where they can utilize their camouflage. Walks stealthy stalking its prey or waits in ambush. Solitary nest built close to ground located in coarse vegetation.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron (juvenile), Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; American Bittern has dark bill.
Similar to: Green Heron. Green Heron has green on it; American Bittern is brown with white stripes.
Similar to: Least Bittern. American Bittern much larger than Least Bittern. Least Bittern has dark cap; American Bittern does not.



Bittern,_Australasian Botaurus poiciloptilus
Description: Mottled brown, black, and buff plumage; buff eyebrow; light throat; dull green face skin, legs, feet.
Distribution: Australia, New Zealand.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Feeds on frogs, eels, and other aquatic creatures. Solitary nest built close to ground located in coarse vegetation.
Status: Endangered.
Image by: 1) John Gerrard Keulemans 2) Nick Talbot - Victoria 3) Wayne_ButterworthDistribution: Australia, New Zealand.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Feeds on frogs, eels, and other aquatic creatures. Solitary nest built close to ground located in coarse vegetation.
Status: Endangered.



Bittern,_Eurasian also Great Bittern Botaurus stellaris
Description: Mainly brown plumage; streaked brown and white breast; black nape, crown; pale buff throat.
Distribution: Europe, Asia, Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Feeds on frogs, eels, and other aquatic creatures. Solitary nest built close to ground; located in coarse vegetation.
Subspecies:
B. s. capensis – southern Africa
B. s. stellaris – temperate Eurasia, tropical Africa
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Steve Chilton 2) Stewart Black - west
of Glastonbury 3) Jan_Svetlik 4) Biopauker - Austria Distribution: Europe, Asia, Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Feeds on frogs, eels, and other aquatic creatures. Solitary nest built close to ground; located in coarse vegetation.
Subspecies:
B. s. capensis – southern Africa
B. s. stellaris – temperate Eurasia, tropical Africa
Status: Least concern.




Bittern,_Pinnated Botaurus pinnatus
Description: Brown upperparts with streaks and barring; white underparts with brown streaks; white throat; greenish-yellow legs. Sexes similarly plumage, but females smaller and have brown instead of black on tail. Length 64–76 cm (25–30 in), weight 554 – 1,157 g (1.2 – 2.6 lb); males weigh more than females.
Distribution: Central and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Eats aquatic creatures.
Subspecies:
B. p. caribaeus – Mexico
B. p. pinnatus – Nicaragua to Ecuador, the Guianas, Argentina, Brazil
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2, 4, 5) Claudio Timm 3) Alastair Rae Distribution: Central and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in densely vegetated wetlands. Eats aquatic creatures.
Subspecies:
B. p. caribaeus – Mexico
B. p. pinnatus – Nicaragua to Ecuador, the Guianas, Argentina, Brazil
Status: Least concern.




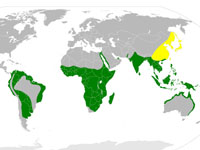
Genus Bubulcus - 1 species
Some split this genus into two species: Bubulcus ibis (western cattle egret) and Bubulcus coromandus (eastern cattle egret). As do most authorities, we treat this genus as containing just one species: Bubulcus ibis (cattle egret). Despite superficial similarities in appearance, the cattle egret is more closely related to the genus Ardea of typical herons than the genus of Egretta of typical egrets.
Egret,_Cattle Bubulcus ibis Found - The Americas, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia.
Description: Nonbreeding has mainly white plumage; yellow bill; greyish-yellow legs. Breeding: eastern subspecies has orange-buff crown, back, breast; red bill, eyes, legs.
Distribution: World wide in tropics, subtropics, and temperate zones. Previously restricted to Spain, Portugal, and Africa; it has undergone one of the most rapid and wide-reaching natural expansions of any bird species.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in open areas such as pastures. Symbiotic relation with cattle. Will follow tractors plowing fields. Eats insects, larvae. Colonial nesters, usually in trees close to water.
Subspecies:
B. i . coromandus – Southeast Asia, India, Australasia
B. i. ibis – Europe, western Asia, New World
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much bigger and has a proportionally longer neck.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. White juvenile Little Blue Heron has bicolored bill; Cattle Egret has yellow bill.
Similar to: Little Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Little Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Snowy Egret has black bill.
Image by: Dick Daniels: 1, 2) Australia 3, 8) North Carolina 4) Puerto Rico 5, 6) Ding Darling National Wildlife Refuge, Sanibel Island 7) Madagascar 10) Boquette, Panama 9) Cristiano Crolle - near Novara, ItalyDistribution: World wide in tropics, subtropics, and temperate zones. Previously restricted to Spain, Portugal, and Africa; it has undergone one of the most rapid and wide-reaching natural expansions of any bird species.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in open areas such as pastures. Symbiotic relation with cattle. Will follow tractors plowing fields. Eats insects, larvae. Colonial nesters, usually in trees close to water.
Subspecies:
B. i . coromandus – Southeast Asia, India, Australasia
B. i. ibis – Europe, western Asia, New World
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much bigger and has a proportionally longer neck.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. White juvenile Little Blue Heron has bicolored bill; Cattle Egret has yellow bill.
Similar to: Little Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Little Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Snowy Egret has black bill.
1, 2, 3, 9) Breeding










Genus Butorides
There are three species of small herons in the genus. All species are about 44 cm (17 inches) long, and have blue-black back and wings, black cap and short yellow legs. Juveniles are browner above and streaked below, and have greenish-yellow legs.
Heron,_Green Butorides virescens
Description: Green back; greenish grey-black wings; greenish-black cap; chestnut neck with white line down the front; grey underparts; yellowish legs. Female smaller than males, somewhat duller and lighter plumage. Juveniles: duller; brown and white streaked head, neck, underparts. Length 41-46 cm (16.1-18.1 in), weight 240 g (8.5 oz), wingspan 64-68 cm (25.2-26.8 in).
Distribution: North and Central America. Breeds mainly east of Mississippi River. Winters mainly Central America. Some year-round at Gulf Coast, southern California coast.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly in small aquatic areas, also at the shore. Eats mainly aquatic prey, also small animals such as mice. Usually stands in shallow water or perches in tree to await prey. Occasionally hovers to spot prey. One of few species to use tools: uses bread crumbs, insects etc. to attract fish. Drowns frogs before eating. Mainly nests in trees, shrubs; sometimes on ground. Pale green eggs.
Subspecies:
B. v. anthonyi - Western US and n Baja California B. v. bahamensis – Bahamas B. v. frazari – S Baja California
B. v. virescens – Central US and e Canada to Panama and Caribbean
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern. Green Heron has green on it; American Bittern is brown with white stripes.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Night-Heron is similar to Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; Green Heron has dark bill.
Similar to: Least Bittern. Green Heron has green on it; Most Least Bittern are brown with white stripes.Adult male Least Bittern is greenish black on back and crown.
Image by: 1, 7) Dick Daniels - North Carolina 2) Dick - California 3) Alan D. Wilson - California 4) Dick - New Jersey 5) Dick - Everglades Natiional Park, Florida 6) Sandy Cole - Flamingo Gardens 7) SCSmithInPhotos - Lakeway, TexasDistribution: North and Central America. Breeds mainly east of Mississippi River. Winters mainly Central America. Some year-round at Gulf Coast, southern California coast.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly in small aquatic areas, also at the shore. Eats mainly aquatic prey, also small animals such as mice. Usually stands in shallow water or perches in tree to await prey. Occasionally hovers to spot prey. One of few species to use tools: uses bread crumbs, insects etc. to attract fish. Drowns frogs before eating. Mainly nests in trees, shrubs; sometimes on ground. Pale green eggs.
Subspecies:
B. v. anthonyi - Western US and n Baja California B. v. bahamensis – Bahamas B. v. frazari – S Baja California
B. v. virescens – Central US and e Canada to Panama and Caribbean
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern. Green Heron has green on it; American Bittern is brown with white stripes.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Night-Heron is similar to Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; Green Heron has dark bill.
Similar to: Least Bittern. Green Heron has green on it; Most Least Bittern are brown with white stripes.Adult male Least Bittern is greenish black on back and crown.
1, 2) Juvenile








Heron,_Lava Butorides sundevalli
Description: Slate-grey plumage which helps it blend in with hardened lava. Breeding: black bill; bright orange legs. Nonbreeding: grey bill, legs.
Distribution: Galapagos Islands.
Habitat: Shoreline, mangrove swamps.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 2) Dick Daniels 3, 4) Putneymark at the Galapagos Distribution: Galapagos Islands.
Habitat: Shoreline, mangrove swamps.
Status: Least concern.




Heron,_Striated also Little Heron also Green-backed Heron Heron,_ s
Description: Blue-grey back, wings; white underparts; black cap; dark line extends from bill to under eye; yellow legs. Juveniles: brown upperparts; streaked underparts.
Distribution: South America, Sub-Saharan Africa, India, east Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found wetlands, edges of water bodies, mangroves. Mainly eats small fish, frogs and aquatic insects. Stands at waters edge to spot prey. May drop leaf to attract prey. Mainly nests in trees, shrubs; sometimes on ground. Pale blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Dwarf Bittern. The Dwarf Bittern has uniform upperparts; Striated Heron has some barring to upperparts
Image by: 1) Cephas 2, 5, 6) Cláudio
Timm - Uruguay 3, 4) Dick Daniels - Australia 5, 8, 9) Dick - Morondava, MadagascarDistribution: South America, Sub-Saharan Africa, India, east Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found wetlands, edges of water bodies, mangroves. Mainly eats small fish, frogs and aquatic insects. Stands at waters edge to spot prey. May drop leaf to attract prey. Mainly nests in trees, shrubs; sometimes on ground. Pale blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Dwarf Bittern. The Dwarf Bittern has uniform upperparts; Striated Heron has some barring to upperparts
1) Juvenile

 ´
´





Genus Cochlearius - 1 species
Heron,_Boat-billed Cochlearius cochlearius
Description: Pale grey upperparts with black upper-mantle; massive black bill; black crown; white face, throat, breast; chestnut belly. Appearance distinctly difference from other herons.
Distribution: Mexico south to Peru, Brazil.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in streams, lagoons, estuaries, mangrove swamps. Captures prey by lunging or using bill as scoop. Eats small fish, shrimp . Prefer to nest colonially. Bluish-white eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Patick Coin 2, 3, 4) Dick Daniels - Jacksonville Zoo 5) Dick - National Aviary
6) Charlie Westerinen - Costa RicaDistribution: Mexico south to Peru, Brazil.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in streams, lagoons, estuaries, mangrove swamps. Captures prey by lunging or using bill as scoop. Eats small fish, shrimp . Prefer to nest colonially. Bluish-white eggs.
Status: Least concern.






Genus Egretta
These species are medium-sized herons, mostly breeding in warmer climates.
Egret,_Chinese Egretta eulophotes
Description: White plumage. Nonbreeding: dusky bill with flesh colored base; yellow-green lores, legs; yellow iris. Breeding: long crest; bright orange bill; blue lores; black legs; yellow feet.
Distribution: East Asia, Japan, Taiwan, Philippines. Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly estuaries, mudflats and bays; also rice fields, fish ponds; breeds on offshore islands.
Status: Vulnerable. Stressed by habitat loss.
Similar to: Little Egret. LIttle Egret has darker legs and bill than Chinese Egret.
Image by: 1) Andres Siani - Bofrneo 2, 3) Jerry Oldenettel - ThailandDistribution: East Asia, Japan, Taiwan, Philippines. Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly estuaries, mudflats and bays; also rice fields, fish ponds; breeds on offshore islands.
Status: Vulnerable. Stressed by habitat loss.
Similar to: Little Egret. LIttle Egret has darker legs and bill than Chinese Egret.



Egret, Dimorphic Egretta dimorpha
Description: Dark blue-grey plumage; yellow feet, facial skin; black legs. White morph.
Distribution: Coastal Kenya, coastal Tanzania, Madagascar, other islands.
Habitat: Coastal aquatic areas.
Image by: 1, 2, 3) Dick Daniels - Antananarivo, Madagascar 4, 5, 6, 7) Dick - Morondava, MadagascarDistribution: Coastal Kenya, coastal Tanzania, Madagascar, other islands.
Habitat: Coastal aquatic areas.







Egret,_Little Egretta garzetta
Description: White plumage; black legs; yellow or black feet. Breeding: blue or red facial skin, long head plumes.
Distribution: Southern Europe, Southern Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Australasia. Appears to be establishing into Gulf Coast of North America.
Habitat and Behavior: Shores of lakes, rivers, canals, ponds, lagoons, marshes. Stalks or ambushes fish, amphibians, and other small prey.
Subspecies:
E. e. garzetta -Eurasia, Africa
E. e. nigripes – Australasia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Little Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Chinese Egret. LIttle Egret has darker legs and bill than Chinese Egret.
Similar to: Dimorphic Egret. If found in Madagascar then Dimorphic Egret.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Little Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Range usually distinguishes between Little Egret and Snowy Egret. However, Little Egrets are sometimes found in the Americas. Adult Snowy Egrets have yellow lores, Little Egrets usually do not.
Image by: 1) Dick - Cairns, Australia 2) DIck Daniels - Plettenberg Bay, South Africa
3, 5) Sandy Cole - St. Lucia, South Africa 4) Cristiano Crolle - Racconigi, Italy 6) Dick - Sylvan Heights 7) Sandy - Sylvan Heights 8) Nik_Borrow 9) Video by Avibirds. More vidoesDistribution: Southern Europe, Southern Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Australasia. Appears to be establishing into Gulf Coast of North America.
Habitat and Behavior: Shores of lakes, rivers, canals, ponds, lagoons, marshes. Stalks or ambushes fish, amphibians, and other small prey.
Subspecies:
E. e. garzetta -Eurasia, Africa
E. e. nigripes – Australasia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Little Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Chinese Egret. LIttle Egret has darker legs and bill than Chinese Egret.
Similar to: Dimorphic Egret. If found in Madagascar then Dimorphic Egret.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Little Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. Range usually distinguishes between Little Egret and Snowy Egret. However, Little Egrets are sometimes found in the Americas. Adult Snowy Egrets have yellow lores, Little Egrets usually do not.
5) The Little Egret, Egyption Geese, and Reed Cormorant kept the crocodile from coming ashore.









Egret, Reddish Egretta rufescens
Description: Dark morph: slate-blue upperparts; reddish head, neck; bluish-black legs, feet. White morph: white plumage; black feet. Juveniles: mainly brown plumage. Length 68–82 cm (27–32 in), wingspan 116–125 cm (46–49 in), weight 364–870 g (0.802–1.918 lb).
Distribution: South USA to northwest South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found shallow aquatic areas. Pursues instead of stalking prey. Eats fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs.
Status: Near threatened.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. White morph Reddish Egret has black legs; juvenile Little Blue Heron has light legs.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. White morph Reddish Egret has black feet; Snowy Egret has yellow feet.
Image by:
1) Barloventomagico - Venezuela 2) Dan Irizarry - Florida 3) Ken Carregan 4) Teddy Llovet - California 5) Alan D. Wilson- Texas 6) Elaine R. Wilson - California 7) Googie Man 8, 9) Dick Daniels - Florida Distribution: South USA to northwest South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found shallow aquatic areas. Pursues instead of stalking prey. Eats fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs.
Status: Near threatened.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. White morph Reddish Egret has black legs; juvenile Little Blue Heron has light legs.
Similar to: Snowy Egret. White morph Reddish Egret has black feet; Snowy Egret has yellow feet.
1) White morph - juvenile 2) White morph - nonbreeding 3) White morph breeding
4) Juvenile 5, 6) nonbreeding 7, 8, 9) breeding









Egret,_Slaty Egretta vinaceigula
Description: Greyish-blue plumage; brown throat, yellow legs. Similar to black egret (Egretta ardesiaca), but slaty egret does not use wings to “shade” prey.
Distribution: Africa – mainly Zambia, Botswana.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers locations where water levels are falling back from rainy season heights. Feeds mainly on fish, but opportunistic.
Status: Vulnerable.
Similar to: Black Heron. Slaty Egret has yellow legs; Black Egret has mostly black legs. Black Egret is more widespread.
Image by: 1, 2) Ian White - Botswana 3) Neil Gray Distribution: Africa – mainly Zambia, Botswana.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers locations where water levels are falling back from rainy season heights. Feeds mainly on fish, but opportunistic.
Status: Vulnerable.
Similar to: Black Heron. Slaty Egret has yellow legs; Black Egret has mostly black legs. Black Egret is more widespread.



Egret, Snowy Egretta thula
Description: all white plumage; black bill, legs; yellow feet. Base of bill yellow but turns red in breeding season. Length 56-66 cm (22.1-26.0 in).
Distribution: Southern North America, Central America, South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands, marshes, riverbanks, lakesides, pools, salt marshes and estuaries; not generally on the coast. Eats fish, crustaceans, insects and other small criters. Stalks or chases prey.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Snowy Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Snowy Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. Juvenile Snowy Egret and juvenile Little Blue Heron are very similar. The upper part of the bill of juvenile Snowy Egret is yellowish; juvenile Little Blue Heron upper part of bill is bluish.
Similar to: Little Egret. Range usually distinguishes between Little Egret and Snowy Egret. However, Little Egrets are sometimes found in the Americas. Adult Snowy Egrets have yellow lores, Little Egrets usually do not.
Similar to: Reddish Egret white morph. White morph Reddish Egret has black feet; Snowy Egret has yellow feet.
Image by: 1) Maggie Smith 2) Len Blumin - California 3) Dick Daniels - Half Moon Bay. California 4) Dick - California 5, 9) Dick - Jamaica 6) Dick - New Jersey 7) Alan D. Wilson - Fulton Harbour,
Fulton, Texas 8) Dick - North Carolina 10) Terry Ross - Texas 11) Dick - South Carolina Distribution: Southern North America, Central America, South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands, marshes, riverbanks, lakesides, pools, salt marshes and estuaries; not generally on the coast. Eats fish, crustaceans, insects and other small criters. Stalks or chases prey.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. Cattle Egret has yellow bill; Snowy Egret has black bill.
Similar to: Great Egret. Great Egret is much larger than Snowy Egret. Great Egret can be distinguished by its yellow bill and black feet.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron juvenile. Juvenile Snowy Egret and juvenile Little Blue Heron are very similar. The upper part of the bill of juvenile Snowy Egret is yellowish; juvenile Little Blue Heron upper part of bill is bluish.
Similar to: Little Egret. Range usually distinguishes between Little Egret and Snowy Egret. However, Little Egrets are sometimes found in the Americas. Adult Snowy Egrets have yellow lores, Little Egrets usually do not.
Similar to: Reddish Egret white morph. White morph Reddish Egret has black feet; Snowy Egret has yellow feet.
1) Juvenile 2, 3, 4) breeding plumage 6 - 11) nonbreeding











Heron,_Black also Black Egret Egretta ardesiaca
Description: Bluish-black plumage; black legs; yellow feet. Breeding: plumes on crown, nape.
Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly eastern part), Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Shallow areas such as ponds and lakes, rice fields, tidal flats. Uses wings umbrella to produce shade which attracts fish. Eats mainly fish; also insects, amphibians, crustaceans.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Slaty Egret. Slaty Egret has yellow legs; Black Egret has mostly black legs. Black Egret is more widespread.
Image by: 1) Dick Daniels - San Diego Zoo 2, 3) Derek_Keats - South Africa 4) Steve
Garvie - The Gambia 5) Ian White - BotswanaDistribution: Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly eastern part), Madagascar.
Habitat and Behavior: Shallow areas such as ponds and lakes, rice fields, tidal flats. Uses wings umbrella to produce shade which attracts fish. Eats mainly fish; also insects, amphibians, crustaceans.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Slaty Egret. Slaty Egret has yellow legs; Black Egret has mostly black legs. Black Egret is more widespread.





Heron,_Little Blue Egretta caerulea
Description: Bluish-grey plumage; blue or greyish bill with black tip; bluish legs, feet. Juveniles have mainly white plumage; dark wing-tips; dull greenish legs. Length 64–76 cm (25–30 in), wingspan 102 cm (40 in), weight 325 g (11.5 oz).
Distribution: The Americas (Gulf states, Central America, Caribbean, south to Peru, Uruguay).
Habitat and Behavior: Found near shallow water (swamps, lagoons, salt marshes, etc.). Eats fish, amphibians, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs. Blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. White juvenile Little Blue Heron has bicolored bill; Cattle Egret has yellow bill.
Similar to: Reddish Egret white morph. White morph Reddish Egret has black legs; juvenile Little Blue Heron has light legs.
Similar to: Snowy Egret juvenile. Juvenile Snowy Egret and juvenile Little Blue Heron are very similar. The upper part of the bill of juvenile Snowy Egret is yellowish; juvenile Little Blue Heron upper part of bill is bluish.
Similar to: Tricolored Heron. Tricolored Heron has some white on its neck and also a white belly; Little Blue Heron does not.
Image by: 1, 2)
Dick Daniels - Jamaica 3, 6) Dick - Puerto Rico
4) Dick - Brookfield Gardens,
South Carolina 5) Dick - Southport, North Carolina Distribution: The Americas (Gulf states, Central America, Caribbean, south to Peru, Uruguay).
Habitat and Behavior: Found near shallow water (swamps, lagoons, salt marshes, etc.). Eats fish, amphibians, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs. Blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Cattle Egret. White juvenile Little Blue Heron has bicolored bill; Cattle Egret has yellow bill.
Similar to: Reddish Egret white morph. White morph Reddish Egret has black legs; juvenile Little Blue Heron has light legs.
Similar to: Snowy Egret juvenile. Juvenile Snowy Egret and juvenile Little Blue Heron are very similar. The upper part of the bill of juvenile Snowy Egret is yellowish; juvenile Little Blue Heron upper part of bill is bluish.
Similar to: Tricolored Heron. Tricolored Heron has some white on its neck and also a white belly; Little Blue Heron does not.
1) Juvenile






Heron,_Pied Egretta picata
Description: Mainly dark grey plumage; black cap; white neck, breast. Juveniles have white head.
Distribution: Northern Australia, New Guinea.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands and grasslands. Eats insects and small aquatic creatures. Nests in trees above water; blue-green eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Jutta234 - Frankfurt Zoo 2) JJ Harrison -
Melbourne Zoo 3) Burtonpe - Adelaide
Zoo, Australia 4) Geoff_WhalanDistribution: Northern Australia, New Guinea.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands and grasslands. Eats insects and small aquatic creatures. Nests in trees above water; blue-green eggs.
Status: Least concern.
4) One adult and rest juveniles




Heron,_Pacicic Reef also Eastern Reef Heron Egretta sacra
Description: Brown bill; gold-yellow eyes; greenish lores. Dark morph: charcoal grey plumage; white stripe on chin. White morph: white plumage. Length 57 to 66 cm (22.2 to 26 in), wingspan 90 to 110 cm (35 to 43 in), average weight 400 grams (14 oz).
Distribution: South Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found: mangroves, coral reefs, beaches, estuaries. Food: fish, crustaceans, mollusks. Pale greenish-blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) John Feather 2, 3)
Glen Fergus - Ladt Elliot Island, Australia 4) Oystercatcher Distribution: South Asia, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found: mangroves, coral reefs, beaches, estuaries. Food: fish, crustaceans, mollusks. Pale greenish-blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Most birds are dark, but there is also a white morph.




Heron,_Tricolored Egretta tricolor
Description: Blue-grey upperparts, head, neck; white line along neck; yellow or grey bill with black tip; white belly. Breeding: long blue plumes.
Distribution: The Americas – east coast USA, Gulf Coast, Caribbean; west coast California to Peru.
Habitat and Behavior: Found swamps and other coastal locals. Eats fish, reptiles, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron. Tricolored Heron has some white on its neck and also a white belly; Little Blue Heron does not.
Image by: 1) Nick Schooley - Florida 2, 3, 6, 10) Dick Daniels - Florida 5. 9) Dick - Lake Okeechobee, Florida 4, 7, 8) Dick - the Carolinas Distribution: The Americas – east coast USA, Gulf Coast, Caribbean; west coast California to Peru.
Habitat and Behavior: Found swamps and other coastal locals. Eats fish, reptiles, crustaceans, insects. Colonial nester in trees and shrubs.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Little Blue Heron. Tricolored Heron has some white on its neck and also a white belly; Little Blue Heron does not.
1) Juvenile










Heron,_Western Reef Egretta gularis
Description: Dark morph (more common) has charcoal grey plumage; whitish throat. Less common morph has white plumage. Usually yellow bill, also black bill. Both morphs: thick yellow legs. Breeding: reddish facial skin, legs; neck plumes.
Distribution: Southern Europe, Africa, parts of Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly on coasts. Often flush prey by running or otherwise moving feet. Also stalks or ambushes fish, amphibians, and other small prey.
Subspecies:
E. g. gularis – coastal west Africa
E. g. schistacea – coastal east Africa, Persian Gulf, southeast India
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Bhardwaj Shanthanu - Kachchh, Gujarat, India 2, 3)
ChriKo near St. Louis, Senegal 4) Nik_Borrow - PrincipeDistribution: Southern Europe, Africa, parts of Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly on coasts. Often flush prey by running or otherwise moving feet. Also stalks or ambushes fish, amphibians, and other small prey.
Subspecies:
E. g. gularis – coastal west Africa
E. g. schistacea – coastal east Africa, Persian Gulf, southeast India
Status: Least concern.




Heron,_White-faced Egretta novaehollandiae
Description: Mainly blue-grey plumage; variable amount of white on face, throat; black lores; yellow legs, feet.
Distribution: Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Shallow fresh or salt waters. Eats mostly aquatic prey; hunts by waiting or stalking. Nests in trees; blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 4, 5, 6) Dick Daniels - Australia 2) David Cook - ACT 3) birdsaspoetryDistribution: Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Shallow fresh or salt waters. Eats mostly aquatic prey; hunts by waiting or stalking. Nests in trees; blue eggs.
Status: Least concern.






Genus Gorsachius
Gorsachius is a genus of Old World night herons typically found near water in forested regions. These are medium-sized herons which are migratory in the colder parts of their ranges, but otherwise resident. They are the least known, most strictly nocturnal, smallest and overall rarest night herons. They feed on crustacean, fish, insects, frogs and other small animals. Night-herons are in genera Gorsachius, Nyctanassa, and Nycticorax.
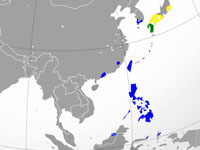
Heron,_Japanese Night- Gorsachius goisagi
Description: Russet head, neck; dark brown wings; black in center of underparts.
Distribution: Japan, Philippines, Indonesia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found dense and damp forests near water. Nocturnal. Eats mainly worms, snails, insects; also crustacean, fish.
Status: Vulnerable.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) Lin_Sun_Fong - Taiwan 3, 4, 5) Ken - Osaka Distribution: Japan, Philippines, Indonesia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found dense and damp forests near water. Nocturnal. Eats mainly worms, snails, insects; also crustacean, fish.
Status: Vulnerable.




Heron,_Malayan Night- Gorsachius melanolophus
Description: Reddish-brown plumage with streaked underparts; blue or black crown; white chin; black bill; greenish legs. Juvenile: greyish and rufous plumage; spotted, vermiculated.
Distribution: southeast Asia, Malaysia.
Habitat and Behavior: Occurs in forests, streams, marshes. Nocturnal, roosts in trees. Usually solitary.Eats mainly earthworms, frogs; also fish.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) Byerly - Taipei City 3) a-giau - Taiwan 4) Ainus 5) KC Hung Distribution: southeast Asia, Malaysia.
Habitat and Behavior: Occurs in forests, streams, marshes. Nocturnal, roosts in trees. Usually solitary.Eats mainly earthworms, frogs; also fish.
Status: Least concern.
1) Juvenile
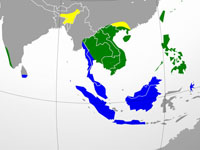




Heron,_White-backed Night- Gorsachius leuconotus
Description: Grey upperparts, head; rufous neck; white eye-ring, lores; red eyes; rufous breast; whitish-brown belly; yellow legs.
Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers dense forests close to streams, lakes,arshes. Nocturnal. Eats crabs, crustacean, fish, insects, frogs and other small animals.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) Francesco Veronesi - Malawi 3) Bernard Dupont - South Africa 4. 5) Nik_BorrowDistribution: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Prefers dense forests close to streams, lakes,arshes. Nocturnal. Eats crabs, crustacean, fish, insects, frogs and other small animals.
Status: Least concern.




Heron,_White-eared Night- Gorsachius magnificus
Description: Mostly blackish-brown plumage; chestnut neck sides; yellow lores; black bill; blackish head, nape. Female similar but head and neck less distinctlvely marked.
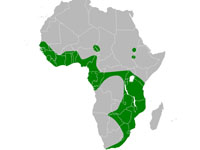
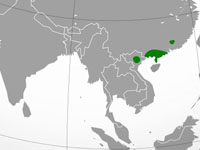
Distribution: southern China and northern Vietnam. Habitat and Behavior: Found subtropical or tropical forests near rivers. Nocturnal. Eats shrimp, fish, frogs.
Status: Endangered.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2, 3) Le Manh Hung - Vietnam 4) Marcel HolyoakDistribution: southern China and northern Vietnam. Habitat and Behavior: Found subtropical or tropical forests near rivers. Nocturnal. Eats shrimp, fish, frogs.
Status: Endangered.
2) Juvenile



Genus Ixobrychus
The Ixobrychus bitterns are all small species, their larger relatives being in the genus Botaurus. They breed in large reedbeds, and can often be difficult to observe except for occasional flight views due to their secretive behaviour. Like other bitterns, they eat fish, frogs, and similar aquatic life.
Bittern,_Black Ixobrychus flavicollis
Description: Black upperparts; yellowish-white neck sides; long yellow bill; brown underparts with white streaks. Juvenile: dark brown rather than black. Length 58 cm (23 in) hus relatively long.
Distribution: Asia, Australasia. Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Nest in platforms of reeds in shrubs, sometime trees.
Subspecies:
I, f.australis – Moluccas, New Guinea and Bismarck Arch., Australia
I. f. flavicollis – India and SE Asia to Indonesia and Philippines I. f. woodfordi – Solomon Islands
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Geoff_Whalan 2) Max Fear 3) Nabarunsadhya 4) Greg MilesDistribution: Asia, Australasia. Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Nest in platforms of reeds in shrubs, sometime trees.
Subspecies:
I, f.australis – Moluccas, New Guinea and Bismarck Arch., Australia
I. f. flavicollis – India and SE Asia to Indonesia and Philippines I. f. woodfordi – Solomon Islands
Status: Least concern.




Bittern,_Black-backed also Australian Little Bittern Ixobrychus dubius
Description: Male black-backed bittern has mainly black upperparts; narrow black cap; chestnut neck, sides of head, underparts; buff shoulder patches. Female dull brown; streaked on back and crown. Length 25 to 36 cm (9.8 to 14.2 in), weight of 60–120 g (2.1–4.2 oz), average weight 84 g (3.0 oz). One of the smallest herons in the world
Distribution: Australia, seasonally New Guinea.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges; sometimes saline wetlands. Usually eats aquatic invertebrates; sometimes fish. Stalks prey at waters edge. Secretive seldom seen. Mainly active dusk or night. Nest supported by reeds; white eggs.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 2) Tom Tarrant - SE Queensland 3) David_CookDistribution: Australia, seasonally New Guinea.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges; sometimes saline wetlands. Usually eats aquatic invertebrates; sometimes fish. Stalks prey at waters edge. Secretive seldom seen. Mainly active dusk or night. Nest supported by reeds; white eggs.
Status: Least concern.
1, 2) Female 3) Male



Bittern,_Cinnamon Ixobrychus cinnamomeus
Description: Male cinnamon bittern has uniform cinnamon colored upperparts; buff underparts. Female similar but back and crown are brown. Juvenile like female but heavily streaked brown underparts. Length 38 cm (15 in), one of the larger Ixobrychus bitterns.
Distribution: Southern Asia, Indonesia, Philippines.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reed beds. Eats fish, amphibian, insects. Difficult to see because of skulking lifestyle. On-guard position when concerned: neck stretched perpendicularly, bill pointing skyward.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Gopi Sundar 2) Francesco Veronesi 3) Matt Francey - Malaysia 4) Malay_Mandal - IndiaDistribution: Southern Asia, Indonesia, Philippines.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reed beds. Eats fish, amphibian, insects. Difficult to see because of skulking lifestyle. On-guard position when concerned: neck stretched perpendicularly, bill pointing skyward.
Status: Least concern.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male




Bittern, Dwarf Ixobrychus sturmii
Description: Dark slate-grey upperparts; blue to yellow-green lores, orbital skin; pale buff throat, dark red to red brown iris; upper-breast; tawny belly streaked dark. greenish yellow to yellow legs.
Distribution: Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found shallow freshwater areas with dense vegetation.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Striated Heron. The Dwarf Bittern has uniform upperparts; Striated Heron has some barring to upperparts.
Image by: 1) Ian White - Botswana 2) Mark Tittley - South Africa Distribution: Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found shallow freshwater areas with dense vegetation.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Striated Heron. The Dwarf Bittern has uniform upperparts; Striated Heron has some barring to upperparts.


Bittern, Least Ixobrychus exilis
Description: White throat and underparts with light brown streaks; brown face, sides of neck; yellow eyes, bill. Male glossy greenish-black back, crown. Female glossy brown back, crown. Smallest member of the family Ardeidae. Length 28 to 36 cm (11 to 14 in), wingspan 41 to 46 cm (16 to 18 in) weight 51 to 102 g (1.8 to 3.6 oz).
Distribution: North America east of Mississippi, Central America, south through Brazil.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Eats fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Hunts with quick jabs of bill while climbing through marsh plants.
Subspecies:
I. e. bogotensis – Central Columbia
I. e. erythromelas – E Panama to the Guianas, se Brazil and Paraguay
I. e. exilis – S Canada to Central America and West Indies
I. e. peruvianus – Peru i. e. pullus – Mexico Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern. American Bittern much larger than Least Bittern. Least Bittern has dark cap; American Bittern does not.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron (juvenile), Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; American Bittern has dark bill.
Similar to: Green Heron. Green Heron has green on it; Most Least Bittern are brown with white stripes.Adult male Least Bittern is greenish black on back and crown.
Image by: 1) Eric Begin - Quebec, CA 2) Ken Schneider - Florida 3) Robert Mathesont - California
4, 5) Mike Baird - Morro Bay, California 6) Mark Vance - Florida 7) Bill Bouton - CaliforniaDistribution: North America east of Mississippi, Central America, south through Brazil.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Eats fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Hunts with quick jabs of bill while climbing through marsh plants.
Subspecies:
I. e. bogotensis – Central Columbia
I. e. erythromelas – E Panama to the Guianas, se Brazil and Paraguay
I. e. exilis – S Canada to Central America and West Indies
I. e. peruvianus – Peru i. e. pullus – Mexico Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern. American Bittern much larger than Least Bittern. Least Bittern has dark cap; American Bittern does not.
Similar to: Black-crowned Night-Heron (juvenile), Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; American Bittern has dark bill.
Similar to: Green Heron. Green Heron has green on it; Most Least Bittern are brown with white stripes.Adult male Least Bittern is greenish black on back and crown.







Bittern, Little Ixobrychus minutus
Description: Short neck; longish bill; buff underparts. Male has black back, crown. Female has browner back; buff-brown wing patch. Length 33–38 cm (13–15 in), wing pan 52–58 cm (20–23 in).
Distribution: Europe, Asia, Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reeds and sedges. Eats fish, amphibians, insects. Nests in reeds, rushes, bushes. Birds that breed in Eurasia migrate in winter to Africa. African birds may be residents. Subspecies: I. m. minutus – Central and s Europe to Siberia; North Africa I. m. payesii – Sub-saharan Africa I. m. podiceps – Madagascar
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Marek Szczepanek 2) Jan Svetlik 3) Mick Sway 4) Ferran Pestana 5) Cristiano Crolle - Annone Lake, Italy Distribution: Europe, Asia, Africa.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reeds and sedges. Eats fish, amphibians, insects. Nests in reeds, rushes, bushes. Birds that breed in Eurasia migrate in winter to Africa. African birds may be residents. Subspecies: I. m. minutus – Central and s Europe to Siberia; North Africa I. m. payesii – Sub-saharan Africa I. m. podiceps – Madagascar
Status: Least concern.
1, 2) Juvenile 3, 4) Female 5) Male





Bittern, Schrenck's Ixobrychus eurhythmus
Description: Male Schrenck’s Bittern has uniform chestnut upperparts; buff underparts; yellow legs, bill. Female has white speckles on chestnut upperparts. Length 33 to 38 cm (13 to 15 in.
Distribution: Asia, Indonesia, Philippines.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Usually eats aquatic invertebrates; sometimes fish. Stalks prey at waters edge. Secretive seldom seen. Mainly active dusk or night.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Naturelly - Singapore 2) OpencageDistribution: Asia, Indonesia, Philippines.
Habitat and Behavior: Mainly located at freshwater with reeds and sedges. Usually eats aquatic invertebrates; sometimes fish. Stalks prey at waters edge. Secretive seldom seen. Mainly active dusk or night.
Status: Least concern.
1) Female 2) Male


Bittern,_Stripe-backed Ixobrychus involucris
Description: Brown upperparts with brown and white stripes; underparts lighter brown striped with white. Length 30 cm (12 in).
Distribution: South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reeds and sedges. Eats small fish,. crustaceans,.insects. Flies infrequently.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) John Gerrard Keulemans 3) Remco_Douma - UruguayDistribution: South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found reeds and sedges. Eats small fish,. crustaceans,.insects. Flies infrequently.
Status: Least concern.


Bittern, Yellow Ixobrychus sinensis
Description: Dull yellow upperparts; chestnut head, neck; buff underparts; black crown. Female’s crown, neck, breast are streaked with brown. Juvenile has heavily streaked underparts. Length 36 to 38 cm (14 to 15 in).
Distribution: Indian Subcontinent east to Japan and Indonesia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly freshwater areas, but also mangroves above high tide. Feeds on insects, fish, amphibians.
Status: Least concern.
Image by:
1) JJ Harrison - Thailand 2) Melvin Yap - Singapore 3) Steven T 4) Tom Tarrant - ThailandDistribution: Indian Subcontinent east to Japan and Indonesia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly freshwater areas, but also mangroves above high tide. Feeds on insects, fish, amphibians.
Status: Least concern.
1, 2) Juvenile 3) female 4) Male




Description: Grey-blue upperparts with black stringy wing pattern; glossy black head with white cheeks and pale yellow crown; black bill.
Distribution: Temperate US, Central America, northern South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Inland marsh, wooded swamp, lakeshores; coastal thickets, mangroves. Mainly bushes, trees for nests; also cliffs. Eats crustaceans, insects, fish and other small prey.
Subspecies:
N. v. bancrofti – Baja California and w Mexico to El Salvador, West Indies
N. v. caliginis – Panama to Peru N. v. cayennensis – Colombia to e Brazil
N. v. gravirostris – islands off w Mexico N. v. pauper – Galapagos Islands
N. v. violacea – Central and e US to e Mexico and Honduras Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern, Green Heron. Juvenile Yellow-crowned Night-Heron is similar to American Bittern and Green Heron. Juvenile Yellow-crowned Heron has small white spots on wings; bitterns do not have white spots.
Similar to Black-crowned Night-Heron. Adult Yelllow-crowned Night-Heron has yellowish crown stripe, Black-crowned Night-Heron does not. Juvenile Black-crowned has pointed, yellowish bill; juvenile Yellow-crowned has dark, non-pointed bill.
Image by: 1) Dick - the Cheasapeak Bay Bridge 2, 3, 4) Dick Daniels - Flamingo Gardens, Florida 5) Sandy Cole - Flamingo Gardens, Florida 6) Dick - Ding Darlng National Wildlife Refuge, Sanibel Island, Florida Distribution: Temperate US, Central America, northern South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Inland marsh, wooded swamp, lakeshores; coastal thickets, mangroves. Mainly bushes, trees for nests; also cliffs. Eats crustaceans, insects, fish and other small prey.
Subspecies:
N. v. bancrofti – Baja California and w Mexico to El Salvador, West Indies
N. v. caliginis – Panama to Peru N. v. cayennensis – Colombia to e Brazil
N. v. gravirostris – islands off w Mexico N. v. pauper – Galapagos Islands
N. v. violacea – Central and e US to e Mexico and Honduras Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern, Green Heron. Juvenile Yellow-crowned Night-Heron is similar to American Bittern and Green Heron. Juvenile Yellow-crowned Heron has small white spots on wings; bitterns do not have white spots.
Similar to Black-crowned Night-Heron. Adult Yelllow-crowned Night-Heron has yellowish crown stripe, Black-crowned Night-Heron does not. Juvenile Black-crowned has pointed, yellowish bill; juvenile Yellow-crowned has dark, non-pointed bill.
1) Juvenile






Genus Nycticorax
Adults are short-necked, relatively short-legged and stout herons; they have a black crown and a whitish belly.
Heron,_Black-crowned Night- Nycticorax nycticorax
Description: black back, crown; white face, throat, breast; grey rest of plumage; red eyes; yellow legs. Juvenile: dull grey-brown plumage on heads, wings, back – with numerous pale spots; paler underparts streaked with brown. Length 58-66 cm (22.8-26.0 in), wingspan 115-118 cm (45.3-46.5 in), weight 727-1014 g (25.6-35.8 oz).
Distribution: The Americas, Sub-Saharan Africa, temperate and tropic Europe, Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found fresh and salt water wetlands. Eats mainly fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Stands still to ambush prey; may use bait to attract prey.
Subspecies:
N. n. falklandicus – Falkland Islands
N. n. hoactli – Canada to Argentina and Chile
N. n. nycticorax – Eurasia south to Indonesia, Africa and Madagascar
N. n. obscurus – N Chile and n-central Argentina to Tierra del Fuego
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern, Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Night-Heron is similar to American Bittern and Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; Green Heron and American Bittern have dark bills.
Similar to Yellow-crowned Night-Heron. Adult Yelllow-crowned Night-Heron has yellowish crown stripe, Black-crowned Night-Heron does not. Juvenile Black-crowned has pointed, yellowish bill; juvenile Yellow-crowned has dark, non-pointed bill.
Image by: 1, 2) Dick Daniels - New Jersey 3, 8) Dick - Brookfield Gardens, So. Carolina 4) Ted
Grussing 5) Chris Queen 6) Sandy Cole - Flamingo Gardens, Florida 7) Dick Daniels- Kauai, Hawaii 9) Dick - Antananarivo, Madagascar 10) Video by Avibirds. More vidoesDistribution: The Americas, Sub-Saharan Africa, temperate and tropic Europe, Asia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found fresh and salt water wetlands. Eats mainly fish, frogs, crustaceans, insects. Stands still to ambush prey; may use bait to attract prey.
Subspecies:
N. n. falklandicus – Falkland Islands
N. n. hoactli – Canada to Argentina and Chile
N. n. nycticorax – Eurasia south to Indonesia, Africa and Madagascar
N. n. obscurus – N Chile and n-central Argentina to Tierra del Fuego
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: American Bittern, Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Night-Heron is similar to American Bittern and Green Heron. Juvenile Black-crowned Heron has mostly yellow bill; Green Heron and American Bittern have dark bills.
Similar to Yellow-crowned Night-Heron. Adult Yelllow-crowned Night-Heron has yellowish crown stripe, Black-crowned Night-Heron does not. Juvenile Black-crowned has pointed, yellowish bill; juvenile Yellow-crowned has dark, non-pointed bill.
1, 2, 3, 4) Juvenile










Heron,_Nankeen_Night- also Rufous Night-Heron Nycticorax caledonicus
Description: Chestnut upperparts; white neck, upper-breast blending to chestnut belly; heavy black bill; white face. Nonbreeding: creamy yellow legs. Breeding: pink legs; grey-black crown; 2 or 3 white plumes from crown. Juvenile: brown-black streaked with beige crown, nape; white with brown streaks neck; rufous-brown tail; green to grey legs feet; olive-yellow bill with black tip.
Distribution: Indonesia, Philippines, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly near rivers, streams; also other aquatic locations. Nocturnal. Eats crustacens, fish, insects. Nest built on ground; male collects stick, female arranges them. Pale blue-green eggs
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cephas 2) flagstaffotos.com.au 2) Michael Spencer - Jurong Bird Park, Singapore 3) Geoff Whalan 4) Mehmet Karatay - Melbourne Zoo
Distribution: Indonesia, Philippines, Australasia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly near rivers, streams; also other aquatic locations. Nocturnal. Eats crustacens, fish, insects. Nest built on ground; male collects stick, female arranges them. Pale blue-green eggs
Status: Least concern.
Description: Mainly white plumage; often yellowish neck; black cap; blue bill, lores. Length 510 and 590 mm, weight 444 to 632 g.
Distribution: Central and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly shallow fresh water locations. Similar to night-herons in behaviour, but less nocturnal.
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1) Cláudio Timm - the Amazon, Brazil 2) Jozeias3d 3) Andreas_TrepteDistribution: Central and South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found mainly shallow fresh water locations. Similar to night-herons in behaviour, but less nocturnal.
Status: Least concern.



Genus Syrigma - 1 species
Heron,_Whistling Syrigma sibilatrix
Description: Grey upperparts, crown; white lower back, tail; whitish neck, underparts; blue orbital skin; pink bill with blue at base, black tip; greenish legs. Length 53 to 64 cm in, weight 521 to 546 g.
Distribution: Colombia, Venezuela, Bolivia to se Brazil and ne Argentina
Habitat and Behavior: Found vicinity of seasonally flooded grasslands. Roosts in trees; perch on posts etc. Eats insects, small animals. Varied hunting techniques: stand still, walk slowly, run. Not colonial nester. Nests in trees; pale blue eggs.
Subspecies:
S. s. fostersmithi – Colombia, Venezuela
S. s. sibilatrix – Bolivia to se Brazil and ne Argentina
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 3) Gustavo Durán - Argentina 2) José Martins 4) Cristiano Crolle Distribution: Colombia, Venezuela, Bolivia to se Brazil and ne Argentina
Habitat and Behavior: Found vicinity of seasonally flooded grasslands. Roosts in trees; perch on posts etc. Eats insects, small animals. Varied hunting techniques: stand still, walk slowly, run. Not colonial nester. Nests in trees; pale blue eggs.
Subspecies:
S. s. fostersmithi – Colombia, Venezuela
S. s. sibilatrix – Bolivia to se Brazil and ne Argentina
Status: Least concern.




Genus Tigriornis- 1 species
Bittern, White-crested also White-crested Tiger-Heron Tigriornis leucolopha
Distribution: African tropical rainforest.
Habitat: Moist lowlands, swamps, streams, rivers, mangroves above high tide.
Status: Least concern.
Image by:
1) Julie DewildeHabitat: Moist lowlands, swamps, streams, rivers, mangroves above high tide.
Status: Least concern.

Genus Tigrisoma
The tiger-herons. Beautiful in flight; great markings on the feathers. Nest that mostly resembles jumble pile of twigs with openings large enough to allow eggs to fall through. Calls sounds like sick cow. A contrast in elegance and coarseness.
Heron,_Bare-throated Tiger- Tigrisoma mexicanum
Description: Blackish upperparts with buff barring; black crown; grey sides of head; white boarded with black median-neck-stripe; dull cinnamon brown underparts.
Distribution: Mexico to northwestern Colombia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in more open habitats than other Tigrisoma herons, such as river and lake banks. Eats fish, frogs or crabs. Often motionless for prey.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Bare-throated Tiger-Heron has barring over more of its body than does Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Juveniles extremely similar.
Image by: 1) Patrick Gijsbers 2. 4) Becky_Matsubara - Costa Rica 3) Dominic Sherony - Limon, Costa Rica 4) Distribution: Mexico to northwestern Colombia.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in more open habitats than other Tigrisoma herons, such as river and lake banks. Eats fish, frogs or crabs. Often motionless for prey.
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Bare-throated Tiger-Heron has barring over more of its body than does Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Juveniles extremely similar.




Heron,_Fasciated Tiger- Tigrisoma fasciatum
Description: Black upperparts and neck with fine buff stripes; black crown; grey sides face, flanks; brown belly; black upper mandible, yellowish-green lower.
Distribution: Costa Rica through northwestern Argentina, southeastern Brazil, and Guyana.
Habitat and Behavior: Primarily in foothills, along rocky, quickly-moving streams. Typically solitary. Hunts on shore or rock. waiting for fish. Also eats insects.
Subspecies:
T. f. fasciatum – SE Brazil to ne Argentina
T. f. pallescens – NW Argentina
T. f. salmoni – Costa Rica to Venezuela and n Bolivia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Bare-throated Tiger-Heron. Bare-throated Tiger-Heron has barring over more of its body than does Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Juveniles extremely similar.
Image by:1) Jerry Oldenettel - Venezuela 2) Dominic Sherony 3) GinaDistribution: Costa Rica through northwestern Argentina, southeastern Brazil, and Guyana.
Habitat and Behavior: Primarily in foothills, along rocky, quickly-moving streams. Typically solitary. Hunts on shore or rock. waiting for fish. Also eats insects.
Subspecies:
T. f. fasciatum – SE Brazil to ne Argentina
T. f. pallescens – NW Argentina
T. f. salmoni – Costa Rica to Venezuela and n Bolivia
Status: Least concern.
Similar to: Bare-throated Tiger-Heron. Bare-throated Tiger-Heron has barring over more of its body than does Fasciated Tiger-Heron. Juveniles extremely similar.



Heron,_Rufescent Tiger- Tigrisoma lineatum Found: Central America, South America
Description: Rufous upperparts, head, neck; fine black vermiculations on lower back; white stripe center of fore neck; short and thick bill; yellow eyes, base of bill; dull green legs. Juvenile: rusty-buff upperparts, coarsely barred with black; white throat, central chest, belly. Length 66–76 cm (26–30 in), weight 630 and 980 g (22 and 35 oz).
Distribution: Central America through much of South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands. usually below 500 m (1600 ft). It is largely crepuscular and generally solitary
Subspecies
T.l. lineatum – Mexico to Amazonian Brazil and n Argentina
T. l. marmoratum – Central Bolivia to e Brazil and ne Argentina
Status: Least concern.
Image by: 1, 5) Cristiano Crolle - Esteros del Iberà, Argentina 2, 3, 4)
Cláudio Timm - the Amazon, Brazil 6) Cristobal Alvarado MinicDistribution: Central America through much of South America.
Habitat and Behavior: Found in wetlands. usually below 500 m (1600 ft). It is largely crepuscular and generally solitary
Subspecies
T.l. lineatum – Mexico to Amazonian Brazil and n Argentina
T. l. marmoratum – Central Bolivia to e Brazil and ne Argentina
Status: Least concern.
1, 2) Juvenile
.jpg)





Genus Zebrilus
Heron,_Zigzag Zebrilus undulatusDescription: Barred brown plumage, lighter on underparts. short legs, neck.
Distribution: Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia.
Habitat and Behavior: Reclusive, even when foraging. Height 32 cm (12.6 in)
Status: Near threatened.
Image by: 1) Joseph Smit 2, 3) Carol Foil - EcuadorDistribution: Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia.
Habitat and Behavior: Reclusive, even when foraging. Height 32 cm (12.6 in)
Status: Near threatened.



Genus Zonerodius - 1 species
Bittern,_Forest Zonerodius heliosylus Found: New Guinea
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) hbw.com