THE WORLD BIRDS - An Online Bird Book
KINGFISHERs of The World - Tree Kingfishers
Order Coraciiformes Family Alcedinidae
KINGFISHERs of The World - Tree Kingfishers
Order Coraciiformes Family Alcedinidae
The kingfisher family Alcedinidae belongs to the Coraciiformes order, as do the bee-eaters of family Meropidae, the motmots of family Momotidae, the rollers of families Brachypteraciidae and Coraciidae, and the todies of family Todidae.
Kingfishers are a group of small to medium sized brightly colored birds in the order Coraciiformes. They have a cosmopolitan distribution, with most species found outside of the Americas. There are about 110 species of kingfisher. All have large heads, long, sharp, pointed bills, short legs, and stubby tails. The typical kingfisher has three toes pointing forward and one to the rear, with the third and fourth toes partially fused together. The bill is usually longer and more compressed in species that hunt fish, and shorter and more broad in species that hunt prey off the ground. Most species have bright plumage with little differences between the sexes. There is also little difference in the length or weight of the sexes. Some species have males slightly larger than females, but other species have the females listed as slightly larger than the males.
The kingfishers are separated into three subfamilies: River Kingfishers (Alcedinina), Tree Kingfishers (Halcyoninae), and Water Kingfishers (Cerylinae). This article is about the Tree Kingfishers.
The tree kingfishers are the most numerous of the three subfamilies in the kingfisher group. There are about 70 species and they are placed into 12 genera, Tree kingfishers are widespread through Asia and Australasia, but also appear in Africa and the islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, utilizing a range of habitats from tropical rainforest to open woodlands. The tree kingfishers are short-tailed large-headed compact birds with long pointed bills. Although some tree kingfishers frequent wetlands, few are specialist fish-eaters. Most species dive onto prey from a perch, mainly taking slow moving invertebrates or small vertebrates.
They are medium sized to large kingfishers. The majority are 20 to 30 cm long. The smallest is the striped kingfisher which is 17 cm long. Paradise kingfisher are much longer than the average kingfisher; they are around 35 cm long. However, much of that is due to their long tails. The biggest of all the kingfishers are kookaburras of genus Dacelo. In fact, the laughing kookaburra with a length of more than 40 cm and weighing up to 450 grams one of the largest kingfishers in the world, right up there with the giant kingfisher of Africa.
The nests are located most often in a cavity located in a tree. This could be a natural tree cavity, or one created by an unrealted bird such as a woodpecker, but most often it is a burrow that the kingfisher created in termite mound. Not only is a termite nest easy to tunnel into to create a kingfisher nest, the termite nest is fertile which attract grasshoppers and other insect. No nest material is added, although litter may build up over the years. Some species create their nest in terrestrial termite mounds and othes tunnel into earth bankings. Both parents incubate the eggs and feed the chicks. Egg laying is staggered at one-day intervals so that if food is short, only the older, larger nestlings get fed.
Genus Actenoides
These kingfisher are in Southeast Asia including Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. They are found in dense forest habitat which makes them difficult to observer. Their diet consists of beetles and other small invertebrates. They are fairly large kingfishers with a length between 20 and 30 cm. Not much is known about their nesting habits, but it seems that some create tunnels in arboreal termite mounds and other creat earthen tunnels.
Kingfisher,_Blue-capped Actenoides hombroni
Description: The male blue-capped kingfisher, also known as Hombron's kingfisher, has a blue crown, mustache, and rump. It has a greenish-blue back and upper-wing coverts. The chin and throat are white, underparts are rufous, and the bill is red. The female has a dull green crown and mustache, olive-green back and upper-wing coverts, and a greenish-blue tail. They are 27 cm in length and weigh about 125 grams with the female slightly larger than the male.
Range: Philippines.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical, moist, lowland forests and montane forests.
Diet: Insects. Also snails, frogs, small reptiles.
Conservation status: The blue-capped kingfisher is listed as vulnerable due to a restricted range and deforestation.
Image by: 1) John Gould Range: Philippines.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical, moist, lowland forests and montane forests.
Diet: Insects. Also snails, frogs, small reptiles.
Conservation status: The blue-capped kingfisher is listed as vulnerable due to a restricted range and deforestation.

Kingfisher,_Green-backed Actenoides monachus Found: Indonesia
Description: The green-backed kingfisher has green upperparts, dark blue head, rufous collar, white throat, chestnut underparts, and red bill. The female has a buffy forehead and face.
Range: Indonesia (Sulawesi and some close islands)
Habitat: Dense tropical moist lowland forests up to 900 m elevation.
Diet: Large centipedes, beetles.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of habitat loss by deforestation
Image by: 1, 3) AS Kono - North Sulawesi 2) Sergey_Yeliseev 4) Ariefrahman - North SulawesiRange: Indonesia (Sulawesi and some close islands)
Habitat: Dense tropical moist lowland forests up to 900 m elevation.
Diet: Large centipedes, beetles.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of habitat loss by deforestation
1) Female 2 - 4) Male




Kingfisher,_Moustached Actenoides bougainvillei Found: Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands
Description: The moustached kingfisher is very rare, seen perhaps once a decade. It has an orange-rufous head, mantle and underparts. It has distinctive blue eye-lines that meet at the nape and also a blue mustache. The wings and tail are dark blue and the bill is red.
Range: Bougainville Island in Papua New Guinea.
Habitat: Dense forest, which make it difficult to observe.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: It is listed as Endangered because it is so infrequently observed.
Image by:
1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) John Gerrard Keulemans Range: Bougainville Island in Papua New Guinea.
Habitat: Dense forest, which make it difficult to observe.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: It is listed as Endangered because it is so infrequently observed.
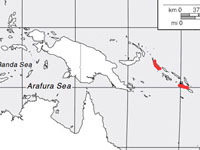

Kingfisher,_Rufous-collared Actenoides concretus
Description: The rufous-collared kingfisher has a black eye-line extending to the nape. There is blue patch on the side of throat and the bill is yellow. The male has a rufous collar, rufous breast, and a green crown. The female has green upperparts, speckled wing coverts, and rufous underparts. It is 22 to 25 cm long and weighs 60 to 90 grams. It excavates a nest-tunnel about 60 cm long, occasionally nest in a rotten tree stump.
Range: Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical moist forest.
Diet: Beetles, cicadas, mantises, spiders, snails. Also fish, reptiles.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of logging.
Image by: 1) Francesco Veronesi - Thailand 2) Jakob Wijkema 3) Mark Benedict - Borneo Range: Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical moist forest.
Diet: Beetles, cicadas, mantises, spiders, snails. Also fish, reptiles.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of logging.
1) Female 2, 3) Male



Kingfisher,_Scaly-breasted Actenoides princeps
Description: The scaly-breasted kingfisher has a dark brown back scalloped with buff. It has a blue head and a reddish-brown collar. The male has whitish-buff underparts with barring on the flanks while the female has darker barring. She also has a buff supercilium. The bill color is variable depending on the region: red, horn colored, or orange and brown. It is 24 cm long.
Range: Sulawesi (Indonesia).
Habitat: Dense understory of undisturbed primary forest.
Diet: Beetles and other small invertebrates.
Conservation status: The scaly-breasted kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss.
Image by: 1, 3, 4) AS Kono 2) JasonbkkRange: Sulawesi (Indonesia).
Habitat: Dense understory of undisturbed primary forest.
Diet: Beetles and other small invertebrates.
Conservation status: The scaly-breasted kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male




Kingfisher,_Spotted Actenoides lindsayi
Description: The male spotted kingfisher has dark green upperparts with each feather tipped with buff giving a spotted effect. It has a dark green crown with black spots, pale blue supercilium, green stripe above the supercilium, and a black band below. The female is similar but less brightly colored and a supercilium green instead of blue. They are 26 cm long.
Range: Philippines.
Habitat: Moist primary forest in both lowland and hilly areas.
Diet: Beetles and other insects, snails and small vertebrates which it probably finds while foraging on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by:
1) John Gould 2) Francesco Veronesi 3) Doing Big Year 4) Noel ReynoldsRange: Philippines.
Habitat: Moist primary forest in both lowland and hilly areas.
Diet: Beetles and other insects, snails and small vertebrates which it probably finds while foraging on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
2) Female 3, 4) Male




Genus Caridonax - 1 species
Kingfisher,_White-rumped Caridonax fulgidus
Description: The white-rumped kingfisher, also known as the glittering kingfisher, has dark blue upperparts, wings, and tail. It has white underparts including the throat. The rump and lower back are also white. The bright white in contrast with the dark blue leads to its "glittering" name. It is 30 cm long. They dig a nest-tunnel in an earth bank.
Range: Indonesia.
Habitat: Prefers primary forests, but some tall trees will also satisfy it.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
iaage by: 1) Abdul_Azis_Gizan Range: Indonesia.
Habitat: Prefers primary forests, but some tall trees will also satisfy it.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: Least Concern.

Genus Cittura - 1 species
Kingfisher,_Lilac Cittura cyanotis
Description: The male lilac kingfisher, also known as the Celebes flat-billed kingfisher, has a brown crown and back, rufous rump and tail, dark blue eye-mask with a white line separating it from the crown, and blue wings. It has whitish underparts, a reddish-brown graduated tail, a large red and flattened bill, and red legs. The female has a black mask. They are 28 cm long.
Range: Indonesia (Sulawesi and some neighboring islands).
Habitat: Forests, especially primary ones. Also, plantations.
Diet: Large insects such as grasshoppers, beetles. Also millipedes and small reptiles.
Conservation status: The lilac kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because primary forests are disappearing.
Image by: 1) A. S. Kono 2) Arihidayat11 3) Francesco Veronesi 4) Jason ThompsonRange: Indonesia (Sulawesi and some neighboring islands).
Habitat: Forests, especially primary ones. Also, plantations.
Diet: Large insects such as grasshoppers, beetles. Also millipedes and small reptiles.
Conservation status: The lilac kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because primary forests are disappearing.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male
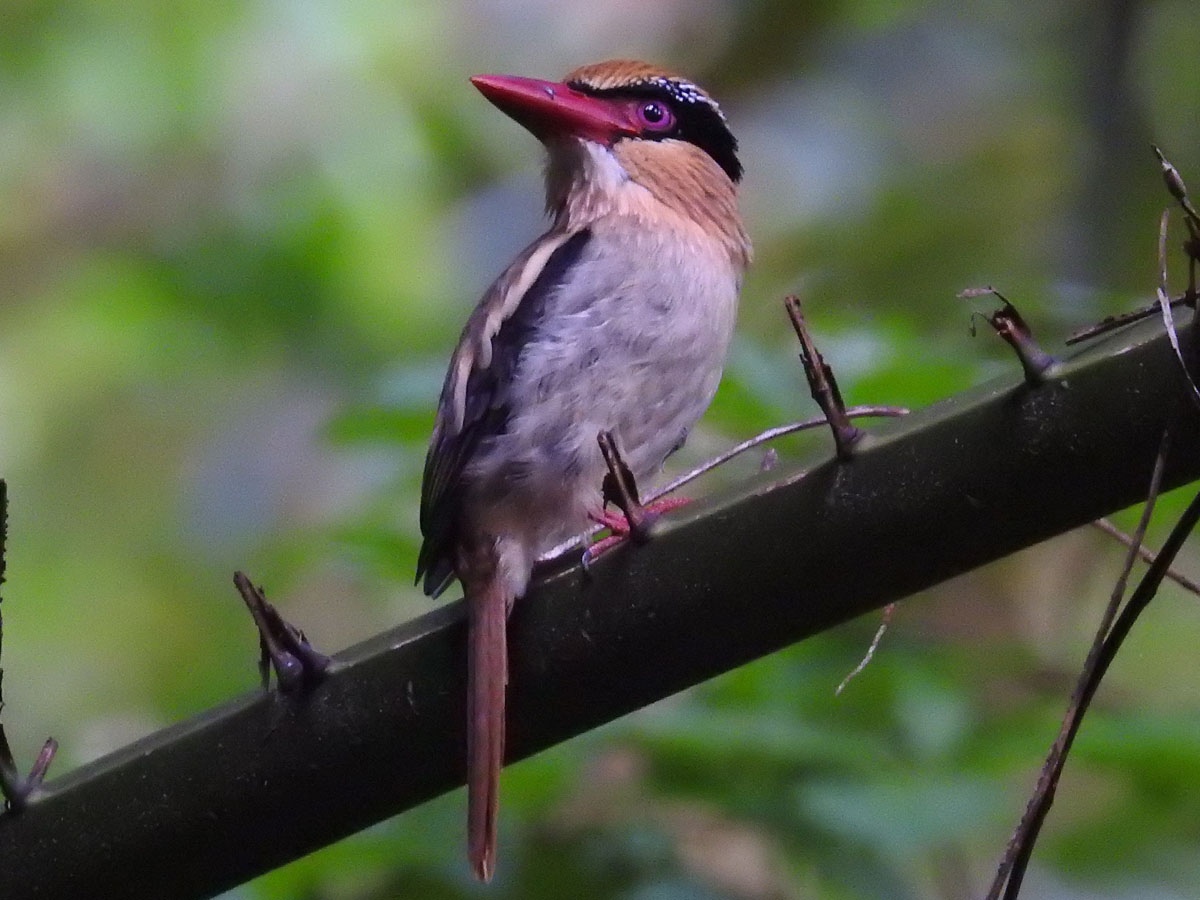




Genus Clytoceyx - 1 species
Kookaburra,_Shovel-billed Clytoceyx rex
Description: The shovel-billed kookaburra, also known as the shovel-billed kingfisher, has dark brown upperparts and head, a rufous stripe behind the eye, white throat, rufous collar and underparts, and a blue rump. It has a heavy, short, thick bill. The male has a dark bluish tail, while the female has a rufous tail. It is 33 cm long and weighs 245 to 325 grams with the female slightly larger than the male.
Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Hill forests.
Diet: Insects, beetles, snails, lizards, earthworms.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) Mark A HarperRange: New Guinea.
Habitat: Hill forests.
Diet: Insects, beetles, snails, lizards, earthworms.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
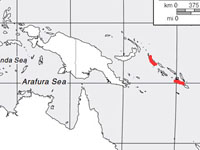

Genus Dacelo
The kookaburra species are found in Australia and New Guinea. Kookaburras eat the young of other birds, mice, snakes, insects and small reptiles. They are very large kingfishers which usually perch in trees to spot their prey on the ground. They usually nest in trees, in either a natural cavity or a termite mound. Some will also nest on the ground in a termite mound.
Kookaburra,_Blue-winged Dacelo leachii
Description: The blue-winged kookaburra has blue wings, a cream colored head with brown streaks, grey-brown mantle, and cream colored underparts with faint vermiculation. The upper-bill is dark, the lower-bill is creamy-yelllow. The male has a blue tail tipped with white. The female has a rufous tail with black bars. They are 38 to 41 cm and 250 to 350 grams with the female a little larger than the male. They nest mainly in a tree cavity on in a termite mound that can be on the ground or in a tree.
Range: Australia, southern New Guinea
Habitat: Open savannah woodland, swamps; also sugarcane plantations.
Diet: In the summer wet season eats mainly insects, lizards and frogs. Other times crayfish, scorpions, spiders, as well as fish, earthworms, small birds and rodents.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Graham_Winterflood - Northern Territory 2) Benjamint444 3) Geoff_Whalan 4) Nik_Borrow. Range: Australia, southern New Guinea
Habitat: Open savannah woodland, swamps; also sugarcane plantations.
Diet: In the summer wet season eats mainly insects, lizards and frogs. Other times crayfish, scorpions, spiders, as well as fish, earthworms, small birds and rodents.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male
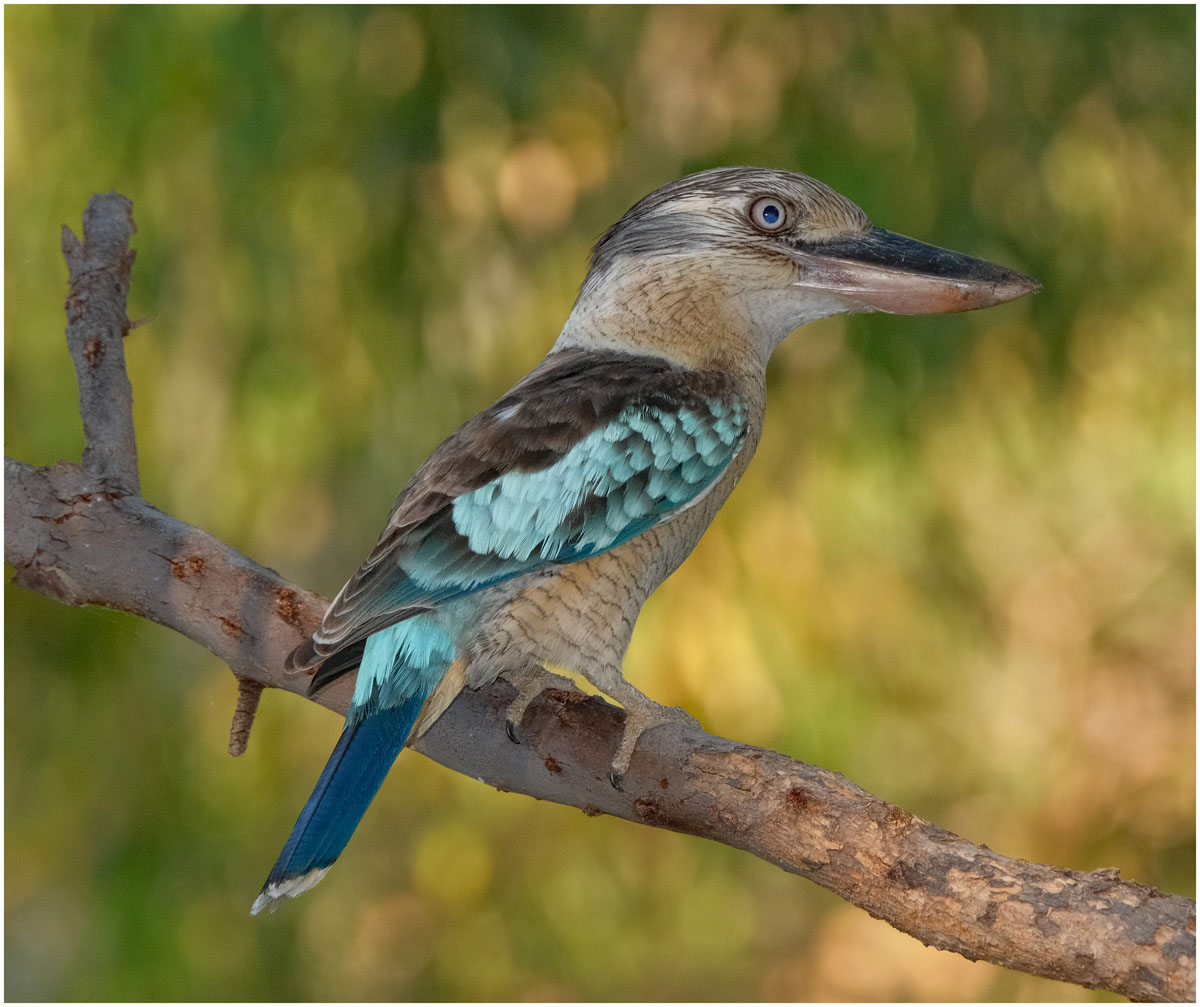




Kookaburra,_Laughing Dacelo novaeguineae
Description: The laughing kookaburra has a white or cream-colored body and head, brown eye-stripe and brown wings. It has a rusty-orange tail with dark brown bars. Their bill is blackish on the top and ivory colored on the bottom. The female has less blue to the rump than the male. The name "laughing kookaburra" refers to the bird's call, which can be heard most frequently at dawn and dusk. It is 39 to 45 cm long and weighs approximately 326 grams with the female larger than the male. They are one of the largest kingfishers. They nest mainly in a natural tree cavity or less frequently in a termite mound which is located on a tree.
Range: Eastern Australia.
Habitat: Open woodland with a grass cover.
Diet: Small mammals, snakes, insects, worms, snails, frogs, small birds.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1, 2) Dick Daniels 3) Toby HudsonRange: Eastern Australia.
Habitat: Open woodland with a grass cover.
Diet: Small mammals, snakes, insects, worms, snails, frogs, small birds.
Conservation status: Least Concern.



Kookaburra,_Rufous-bellied Dacelo gaudichaud
Description: The rufous-bellied kookaburra has a black cap, white collar, white bill, black mantle, blue wing-coverts, and rufous underparts. The male has a blue tail tipped with white, while the female has a rufous tail. They are 28 cm long and weigh about 140 grams which makes them the smallest of the kookaburras, but still a very large kingfisher. They build a tunnel-nest in a termite nest located high up in a tree.
Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Dense rainforest.
Diet: Grasshoppers, beetles, spiders, larvae. Also small reptiles. mammels, and birds.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1, 2) Nik Borrow 3) Greg_MilesRange: New Guinea.
Habitat: Dense rainforest.
Diet: Grasshoppers, beetles, spiders, larvae. Also small reptiles. mammels, and birds.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
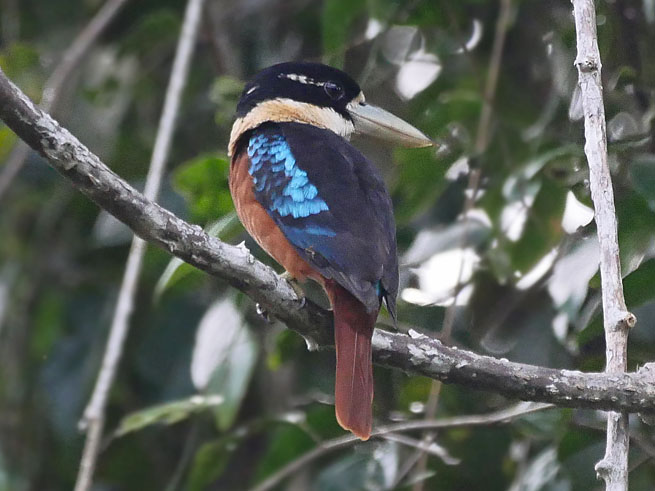



Kookaburra,_Spangled Dacelo tyro
Description: The spangled kookaburra has a white spotted black head, dark grey upper-bill and white lower-bill. It has bright blue wings, a blue tail, and white underparts, It is 33 cm long and about 150 grams with the female slightly larger than the male. They build a tunnel-nest in a termite nest located usually in a tree.
Range: Southern New Guinea .
Habitat: Wooded savanna, forests.
Diet: Insects such as beetles and ants.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) John Gould 2) Doug Janson - Jurong Bird Park, SingaporeRange: Southern New Guinea .
Habitat: Wooded savanna, forests.
Diet: Insects such as beetles and ants.
Conservation status: Least Concern.


Genus Halcyon
“sit and wait” predators of small ground animals including large insects, rodents, snakes, and frogs, but some will also take fish. They are found mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa. Like other kingfishers, the Halcyon kingfisher are cavity nesters. Some excavate tunnels in a slope such as a banking or gulley, other use an active termite nest which is usually located in a tree, but could also be on the ground. All of the species in this genus are listed as Least Concern.
Kingfisher,_Black-capped Halcyon pileata
Description: The black-capped kingfisher has a blue back and tail, plus a black crown and wings. It has a white neck, throat, and breast. The belly is rufous; the legs and bill are red. It is 28 to 32 cm long and weighs about 80 grams. The pair excavate a tunnel 50 to 100 cm long in a streambank; also uses a termite mound.
Range: Tropical Asia and Southeast Asia.
Habitat: Mainly near the coast in mangrove forests and along estuaries and rivers.
Diet: Inland it feeds on insects; coastal on fish and crabs. Perches and then dives for prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) JJ Harrison - Thailand 2) LonelyShrimp 3, 4) Frankie ChuRange: Tropical Asia and Southeast Asia.
Habitat: Mainly near the coast in mangrove forests and along estuaries and rivers.
Diet: Inland it feeds on insects; coastal on fish and crabs. Perches and then dives for prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




Kingfisher,_Blue-breasted Halcyon malimbica
Description: The blue-breasted kingfisher has a blue head, back, wing panel, and tail. It has white underparts with a blue breast-band, black shoulders and eye-line, red upper-bill, and black lower-bill. It is 25 cm long. They usually build a nest in a termite mound that is located in a tree.
Range: West Afica.
Habitat: Forests, wooded savanna.
Diet: Mainly invertebrates such as cockroaches, grasshoppers, termites, centipedes. Also, fish, frogs, small birds and reptiles.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) JV Verde - The Gambia 2, 3, 4) Nik Borrow -Ghana, Ghana, UgandaRange: West Afica.
Habitat: Forests, wooded savanna.
Diet: Mainly invertebrates such as cockroaches, grasshoppers, termites, centipedes. Also, fish, frogs, small birds and reptiles.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




Kingfisher,_Brown-hooded Halcyon albiventris
Description: The male brown-hooded kingfisher has a dark brown head, back, and wings. It has a buff neck and underparts. He has some dark streaks on the head and breast. The tail and primary feathers are turquoise, while the bill and feet are red. The female has light brown instead of dark brown. It is 23 cm long, weighs about 50 grams, and the female is slightly larger than the male. The similar grey-headed kingfisher has a chestnut belly. They excavate a nest-tunnel about 1 meter long in a slope such as a banking or gulley.
Range: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Woodland, scrubland, forest edges, and also suburban areas.
Diet: Insects; also scorpions, reptiles, small birds, rodents and fish. Perches searching the ground for prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Sias van Schalkwyk - South Africa 2) Arno Meintjes 3) Dick - South Africa 4) Nik_Borrow - MalawiRange: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Woodland, scrubland, forest edges, and also suburban areas.
Diet: Insects; also scorpions, reptiles, small birds, rodents and fish. Perches searching the ground for prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male




Kingfisher,_Chocolate-backed Halcyon badia
Description: The chocolate-backed kingfisher has a brownish-black mantle, black back, dark brown head and hind-neck, blue rump, white throat, and white underparts. It has a bright blue speculum. The bill is red and the legs are purplish red. It is 21 cm and weighs about 60 grams. They create their nests from termite nests that the termites constructed on an angled branch or vine.
Range: Western Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Primary and secondary lowland rain forest.
Diet: Insects, mainly grasshoppers and beetles, but also many other invertebrates as well as small lizards.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Walter_Jetz 2, 3) Nik Borrows - Ghana, UgandaRange: Western Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Primary and secondary lowland rain forest.
Diet: Insects, mainly grasshoppers and beetles, but also many other invertebrates as well as small lizards.
Conservation status: Least Concern.



Kingfisher,_Grey-headed Halcyon leucocephala
Description: The grey-headed kingfisher has a grey head and nape plus a black back and wings. It has a chestnut belly, turquoise primary wing feathers and tail. The bill is red as are the legs. The similar brown-hooded kingfisher has a white or light belly. It is 21 cm long. The pair excavates a 40 to 100 cm long nest-tunnel in a slope such as a banking or gulley. Also known to use a termite nest.
Range: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Scrub and dry woodlandl; often found near water, but it s is not aquatic.
Diet: Mainly insects such as grasshoppers and beetles. Looks for prey from a perch. Most prey are taken the ground, but some in flight.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Gip Gipukan 2) Alastair Rae 3) Arno Meintjes 4) Nik_Borrow - EthiopiaRange: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Scrub and dry woodlandl; often found near water, but it s is not aquatic.
Diet: Mainly insects such as grasshoppers and beetles. Looks for prey from a perch. Most prey are taken the ground, but some in flight.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




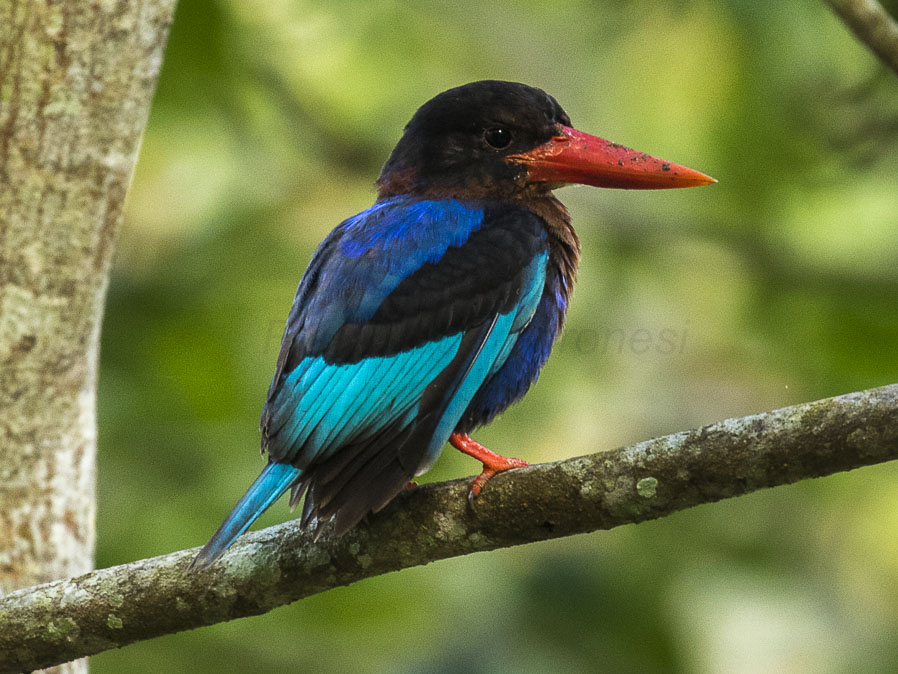
Kingfisher,_Javan Halcyon cyanoventris
Description: The Javan kingfisher has a black head, rufous collar and upper-breast. The rest of the underparts are blue. The wings are turquoise with back upper-wing coverts. The tail is also turquoise. It has a red bill and legs. The Javan kingfisher is 26 cm long. They excavate a 100 cm long nest-tunnel in a slope such as a banking or gulley.
Range: Java and Bali of Indonesia.
Habitat: Relatively open areas such as mangroves, dry forest, gardens, and parks.
Diet: Mainly insects; also larvae, shrimp.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by:
1) Ken San- Bali Bird Park 2) Francesco_Veronesi 3) Eko_PrastyoRange: Java and Bali of Indonesia.
Habitat: Relatively open areas such as mangroves, dry forest, gardens, and parks.
Diet: Mainly insects; also larvae, shrimp.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
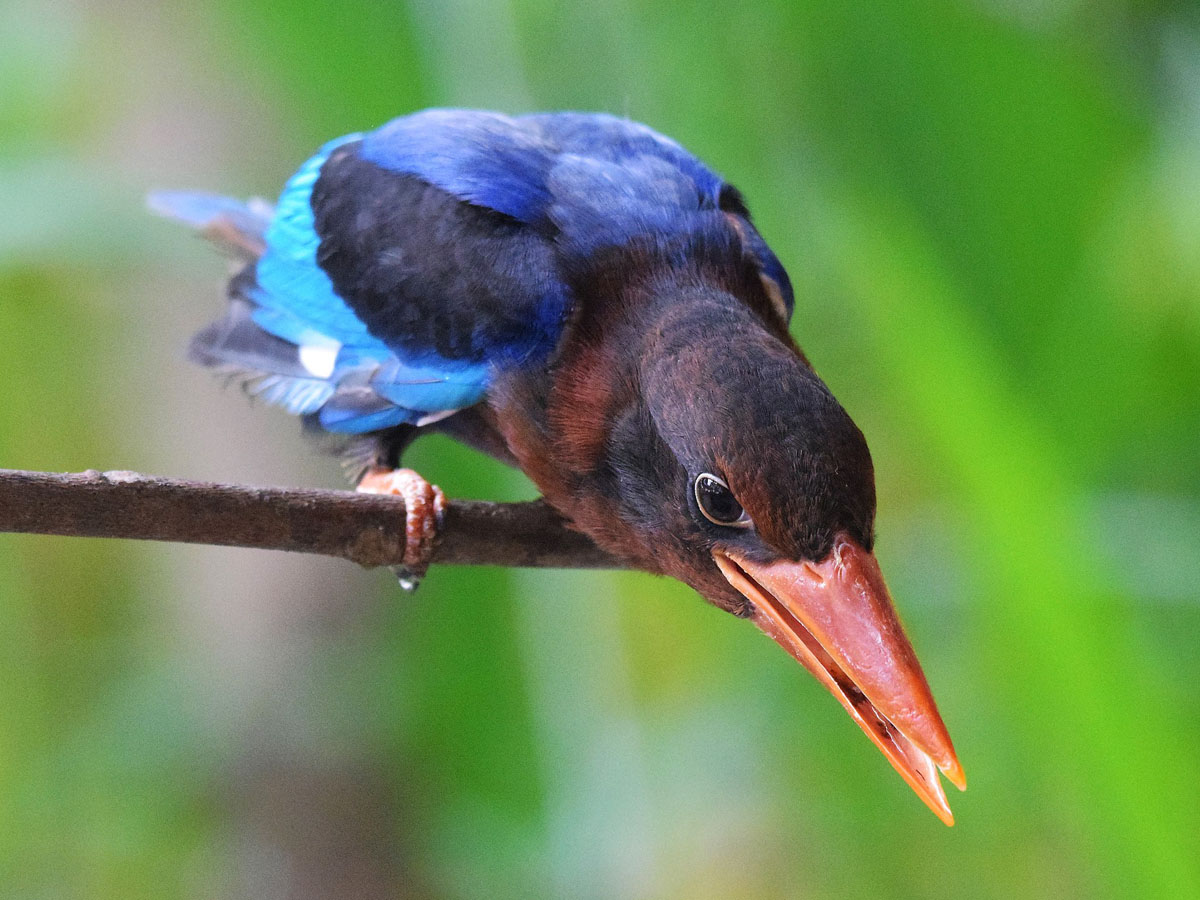



Kingfisher,_Mangrove Halcyon senegaloides
Description: The mangrove kingfisher has a blue back and tail. The shoulders, wings, and lores are black. It has a pale grey to white head, neck, and underparts. The bill is red and the legs are dark grey-brown. The similar woodland kingfisher has a red upper mandible and black lower mandible. It is 22 cm in length and weighs 57 to 66 grams. Nests in tree cavity, tunnel in riverbank, or arboreal termite nest.
Range: East Africa.
Habitat: Woodlands, preferably near water; wooded estuaries and mangroves in non-breeding season.
Diet: Fish, crustaceans, lizards, insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Paul Barnard - Zambia 2) Stephen_Temple - South Africa 3) Ian White - Zambia 4) Nik_Borrow - TanzaniaRange: East Africa.
Habitat: Woodlands, preferably near water; wooded estuaries and mangroves in non-breeding season.
Diet: Fish, crustaceans, lizards, insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
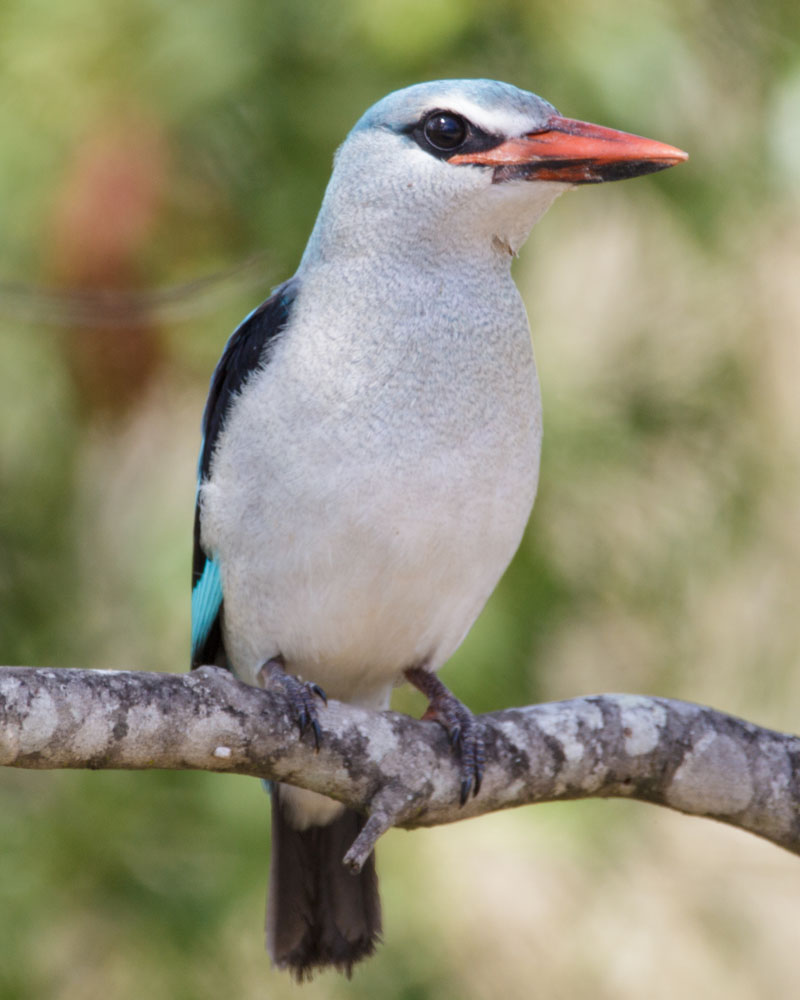




Kingfisher,_Ruddy Halcyon coromanda
Description: The ruddy kingfisher has a rust-red body which deepens to purple at the tail. It has a red bill and legs. It is 25 cm in length which is long for its genus. Some of the extra length is due to its very long bill.
Range: South Korea and Japan in the north, south through the Philippines to the Sunda Islands, and west to China and India.
Habitat: Heavily forested areas.
Diet: Fish, crustaceans, large insects. Also frogs and other amphibian.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Yasaiman 2) Changhua Coast Conservation 3) Jason_Thompson - Thailand 4) Hiyashi_Halso known asRange: South Korea and Japan in the north, south through the Philippines to the Sunda Islands, and west to China and India.
Habitat: Heavily forested areas.
Diet: Fish, crustaceans, large insects. Also frogs and other amphibian.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
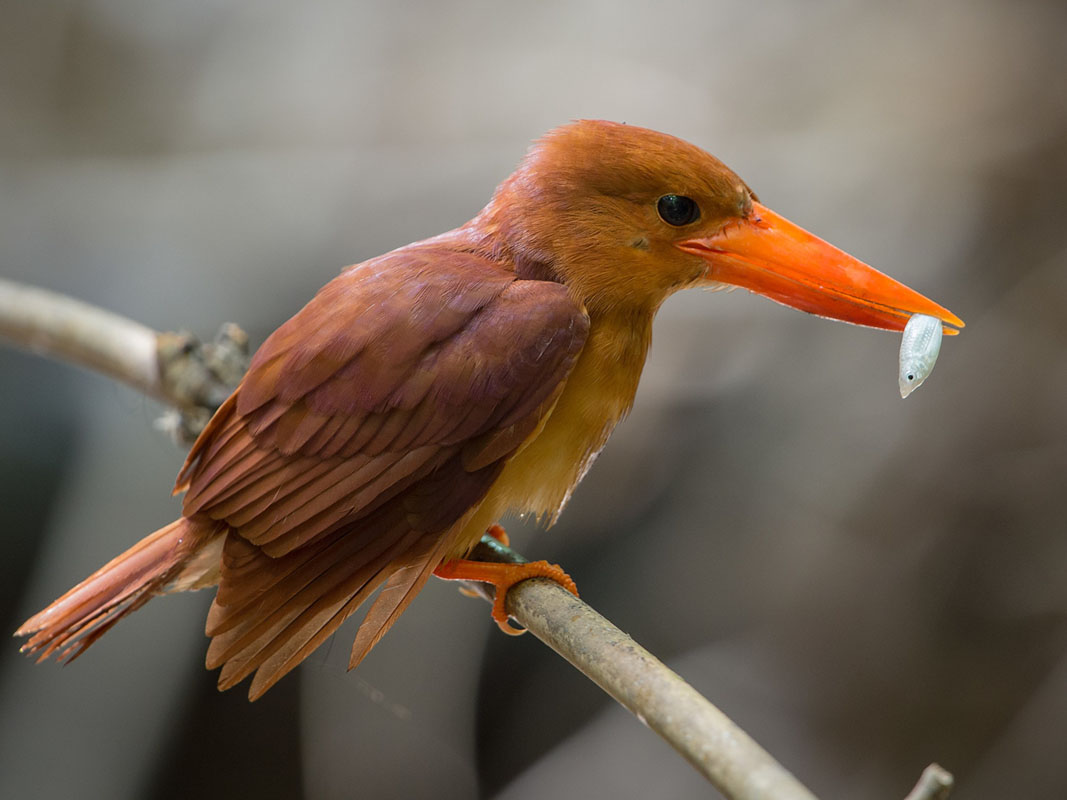




Kingfisher,_Striped Halcyon chelicuti
Description: The striped kingfisher has greyish-brown upperparts, off white underparts, and a streaked brown crown (male has buffy-grey background on the head, female has brownish background), The lower back, secondary flight feathers, and tail are metallic blue which is striking when the bird flies. The upper-bill is black and the lower-bill is red. They are 17 cm in length, male weighs 30 to 40 grams, female 37 to 50 g. The striped kingfisher uses vacant woodpecker or barbet nesting cavities.
Range: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Woodland, thorn scrub, dry bush, and open savanna.
Diet: Mainly grasshoppers and other large insects. Also lizards, snakes, rodents. Hunts from a perch about 3 meters above the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Derek_Keats - South Africa 2) Dick Daniels - Fish Eagle Lodge, Knysna Lagoon 3, 4) Nik_BorrowRange: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Woodland, thorn scrub, dry bush, and open savanna.
Diet: Mainly grasshoppers and other large insects. Also lizards, snakes, rodents. Hunts from a perch about 3 meters above the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
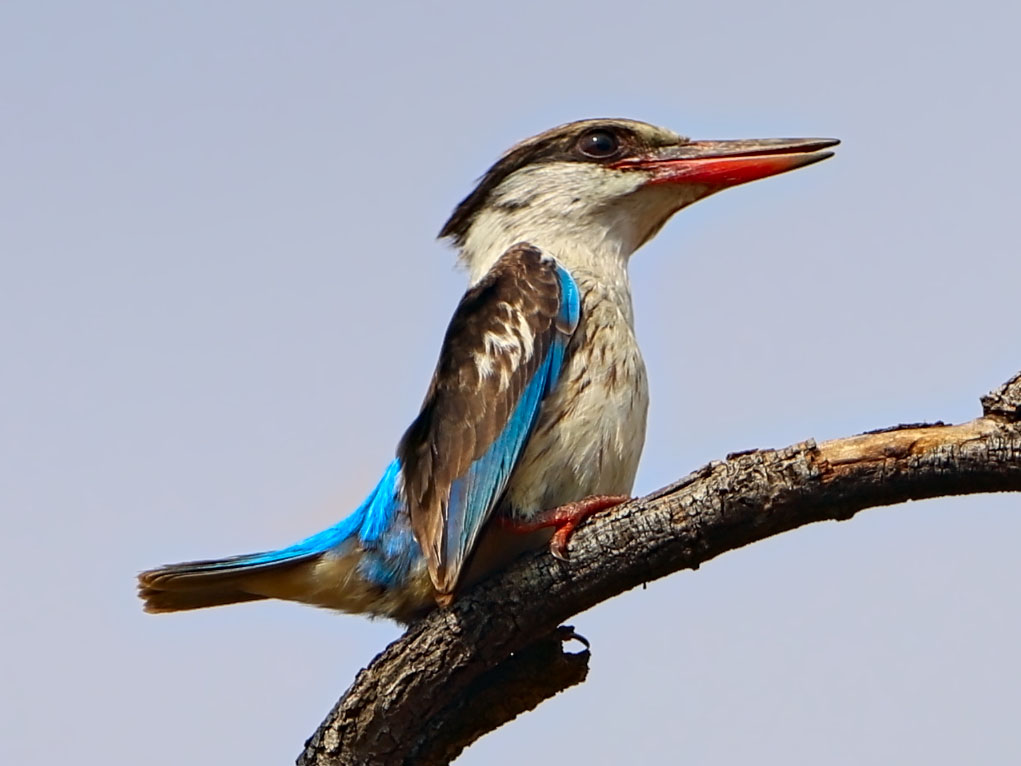




Kingfisher,_White-throated Halcyon smyrnensis
Description: The white-throated kingfisher, also known as the white-breasted kingfisher, has a bright blue back, wings, and tail The head and underparts are chestnut except for the white throat and breast. It has a red bill and legs. This is a large kingfisher with a length of 27 cm. The female is larger than the male. The pair excavates a 30 to 150 cm long nest-tunnel in a slope such as a banking or gulley. Also known to use a termite nest.
Range: Southern Asia.
Habitat: A wide variety of habitats, but avoids dense forest.
Diet: Insects, fish, reptiles, amphibians, crabs, small rodents, birds. From a perch it dives to the water or ground for its prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Koshy_Koshy - India 2, 3) Dick - San Diego Zoo 4) Ansel.MaRange: Southern Asia.
Habitat: A wide variety of habitats, but avoids dense forest.
Diet: Insects, fish, reptiles, amphibians, crabs, small rodents, birds. From a perch it dives to the water or ground for its prey.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




Kingfisher,_Woodland Halcyon senegalensis
Description: The woodland kingfisher has a bright blue back and tail. It has black shoulders and upper-wing coverts. The forehead, crown, and nape are brownish-grey. It has a red upper mandible, red legs, black lower mandible, and white belly. It is 23 cm long, male weighs 41 to 60 grams, and female weighs 55 to 64 g. They usually use and exiting tree cavity. The similar mangrove kingfisher bill is entirely red.
Range: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Variety of wooded habitats with some trees.
Diet: Mainly large insects such as grasshoppers. Also fish, frogs, lizards.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Dick Daniels - Tanzania 2)
Arno Meintjes 3) Dick - San Diego Zoo 4) Nik_Borrow - GhanaRange: Sub-Saharan Africa.
Habitat: Variety of wooded habitats with some trees.
Diet: Mainly large insects such as grasshoppers. Also fish, frogs, lizards.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




Genus Melidora - 1 species
Kingfisher,_Hook-billed Melidora macrorrhina
Description: The male hook-billed kingfisher has brown upperparts with buff tips, black crown feathers with blue tips, black upper mandible, horn lower mandible, hooked tip of bill, and whitish underparts. There is a long white stripe below the eyes. The female has green fringes to the crown, and buffy underparts. It is 27 cm long and weighs 85 to 110 grams. It constructs its nest in an arboreal termite nest.
Range: New Guinea and some nearby islands.
Habitat: Primary forests and also much less wooded areas.
Diet: Insects, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1, 2, 3) Katerina_Tvardikova 4) Nik_BorrowRange: New Guinea and some nearby islands.
Habitat: Primary forests and also much less wooded areas.
Diet: Insects, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
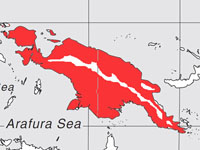



Genus Syma
These two species are found in New Guinea and close islands.
Kingfisher,_Mountain Syma megarhyncha
Description: The mountain kingfisher has greenish-blue upperparts, blue-green rump, and blue tail. It has an orange-yellow bill, orange head, orange nape, a black nape patch, and a white throat. The female has a black crown. The mountain kingfisher is found in highlands, while the similar yellow-billed kingfisher is found in lowlands. It is 21 to 24 cm in length.
Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Forests above 1200 meters.
Diet: Insects, larvae, lizards. Perches on a branch before going for the prey on a leaf or on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Planet Earth 2) Katerina_Tvardikova 3) Nik_BorrowRange: New Guinea.
Habitat: Forests above 1200 meters.
Diet: Insects, larvae, lizards. Perches on a branch before going for the prey on a leaf or on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1, 2) Female 3) Male
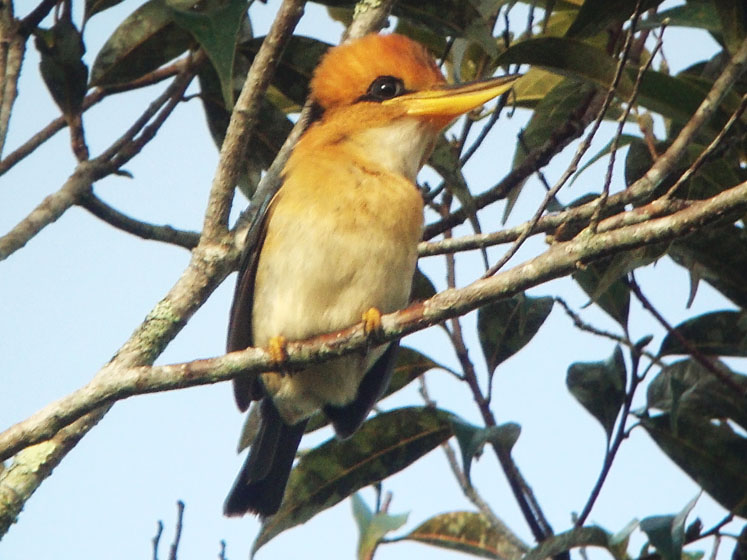



Kingfisher,_Yellow-billed Syma torotoro
Description: The yellow-billed kingfisher has a blackish upper-mantle, green lower back, blue-green rump, and blue tail. It has an orange-yellow bill, orange head, orange nape, and black nape patch. The throat is white and the underparts are pale orange-grey. The female has a black crown patch. It is 20 cm in length and weighs 30 to 50 grams. The yellow-billed kingfisher is found in lowlands while the similar mountain kingfisher is found in highlands.
Range: New Guinea and adjacent islands.
Habitat: Lowland rainforest and along forest edges.
Diet: Insects, lizards, worms.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Markaharper 2) Brian_McCauley 3) Nik_Borrow Range: New Guinea and adjacent islands.
Habitat: Lowland rainforest and along forest edges.
Diet: Insects, lizards, worms.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1 - 3) Male



Genus Tanysiptera
The paradise-kingfishers are so named because of their tails which have elongated central feathers. In some species the elongated feathers have wide ends that are termed paddles or racquets. Most of the paradise-kingfishers live in New Guinea or nearby islands. The buff-breasted paradise-kingfisher migrates between New Guinea and northern Australia.
Paradise-kingfishers nest in termite mounds. Some species choose mounds that are on the ground while others prefer arboreal nests. In either case, an active nest is selected because they have more structural integrity than abandoned termiite nests. The surface of an active termite nest is hard. The paradise-kingfishers penetrate this hard outer surface by flying repeatedly into the nest with their strong and wedge shaped red bill. When the surface has been sufficiently penetrated, they use their feet to excavate a tunnel which ends in an egg chamber about 13 cm in diameter. Their feet are specialized for excavation - the third and fourth toes are fused together for added strength. Both pair incubate the eggs and then feed the young until they are ready to fledge after about 25 days.
Paradise-kingfishers favorite food are insects, which is not surprising since they grow up in a nest created by an insect. Plus termite nests are created by decaying plant material which is very fertile and helps the ecosystem around it to support other insects such as grasshoppers and beetles. Most of the species rarely feed on fish so their habitat does not require water sources close by. Instead they need primary or secondary forests with a supply of active termite nests.
Kingfisher,_Biak Paradise- Tanysiptera riedelii
Description: The Biak paradise-kingfisher has glossy turquoise-blue upperparts, crown, and nape. It has a white rump, black under-wings, red bill, and white underparts. It is 37 cm long, including its tail and weighs about 65 grams.
Range: Biak Island in Indonesia.
Habitat: Primary forest, and perhaps also disturbed forest.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened as little is known about its distribution.
Image by: 1) Biodiversity Heritage Library 2) Ross_TsaiRange: Biak Island in Indonesia.
Habitat: Primary forest, and perhaps also disturbed forest.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened as little is known about its distribution.
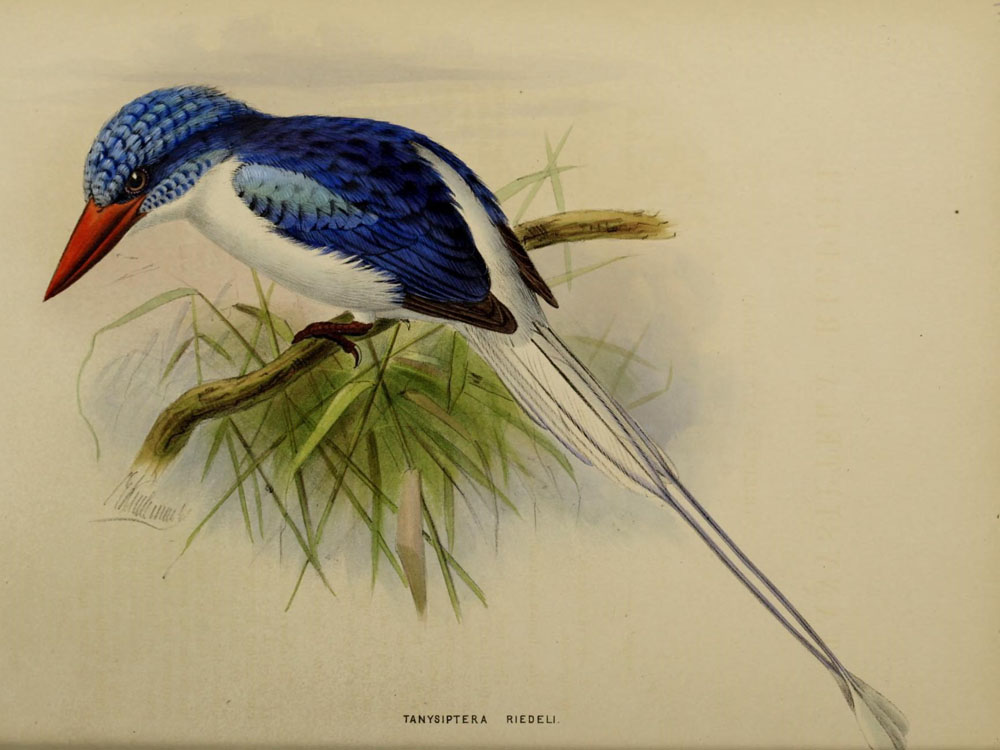
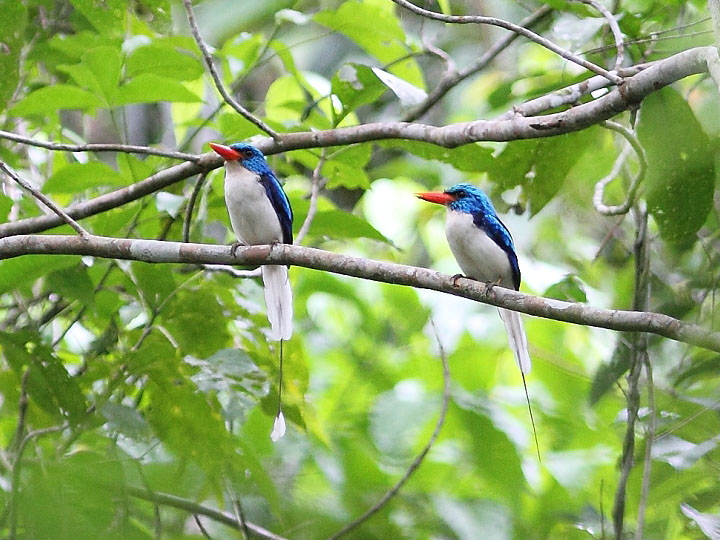


Kingfisher,_Black-capped_Paradise- Tanysiptera nigriceps
Description: The black-capped paradise-kingfisher, also known as black-headed paradise-kingfisher, has a black head, black nape, blue wings, blue outer tail covers, pale yellowish-buff underparts, plus orange bill and feet. It is 35 to 48 cm long including its tail.
Range: Bismarck Archipelago which is to the east of New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests, forest edges.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1, 2)
Nik_BorrowRange: Bismarck Archipelago which is to the east of New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests, forest edges.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Least Concern.


Kingfisher,_Brown-headed_Paradise- Tanysiptera danae
Description: The male brown-headed paradise-kingfisher has a rufous-brown head and mantle. It has reddish-pink underparts including the throat. It has red bill and legs. The female has a buff chin and throat. They are 23 cm long excluding the tail which adds up to 9 cm to its length.
Range: Papua New Guinea.
Habitat: Tropical moist lowland forests.
Diet: Mainly insects which it catches on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by:
1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) Markaharper 3, 4) Nik BorrowRange: Papua New Guinea.
Habitat: Tropical moist lowland forests.
Diet: Mainly insects which it catches on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
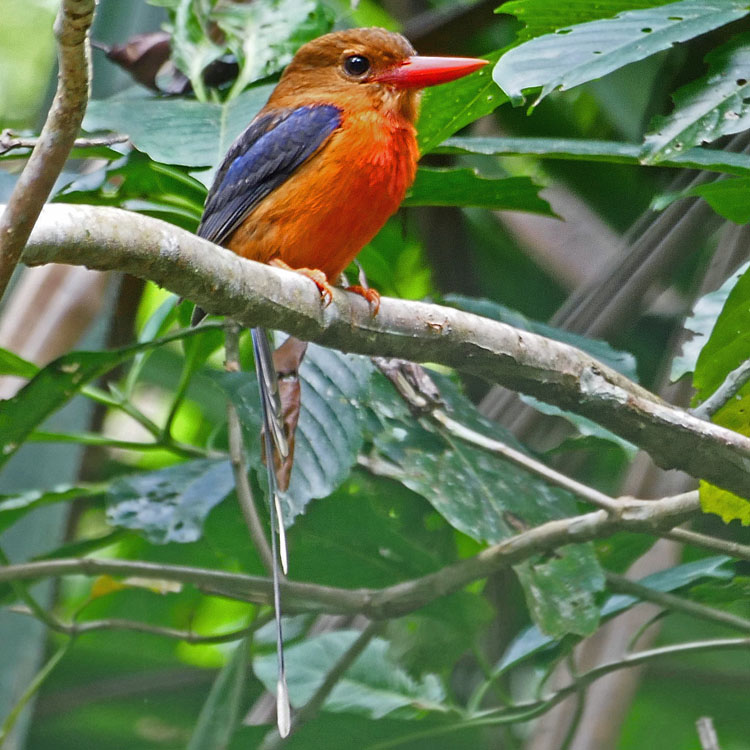
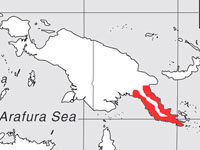



Kingfisher,_Buff-breasted Paradise- Tanysiptera sylvia
Description: The buff-breasted paradise-kingfisher has a blue crown, black eye-stripe which continues to the nape, rufous underparts, red bill, and red feet. It has a white lower back, white rump, and a white patch on the center of its back. There are long white or blue-and-white tail feathers, It is 35 cm long including the tail feathers. Tails vary in length but are approximately 18 cm. They usually excavate their nest in terrestrial termite nests, but sometimes in arboreal termite nests.
Range: New Guinea and the northern coast of Australia.
Habitat: Lowland monsoon rainforest, and isolated patches of hill forest in areas where there are active termite mounds suitable for nesting.
Diet: Invertebrates such as grasshoppers, beetles. Also bees, earthworms, centipedes.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by:
1)) Graham_Winterflood 2) Jim_Bendon 3) Brian_McCauleyRange: New Guinea and the northern coast of Australia.
Habitat: Lowland monsoon rainforest, and isolated patches of hill forest in areas where there are active termite mounds suitable for nesting.
Diet: Invertebrates such as grasshoppers, beetles. Also bees, earthworms, centipedes.
Conservation status: Least Concern.



Kingfisher,_Common_Paradise- Tanysiptera galatea
Description: The common paradise-kingfisher has dark blue upperparts, a blue crown, white rump, and white underparts. The tail is blue with white edges. It has a red bill. The female is similar to the male but smaller, especially the tail. They are 33 to 43 cm long, including the tail. They excavate their nest in arboreal termite nests, The similar buff-breasted paradise-kingfisher has more white on its tail.
Range: New Guinea and nearby islands.
Habitat: Lowland forests.
Diet: Mainly earthworms; also insects and snails.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Francesco Veronesi - Halmahera 2) Nik_BorrowRange: New Guinea and nearby islands.
Habitat: Lowland forests.
Diet: Mainly earthworms; also insects and snails.
Conservation status: Least Concern.


Kingfisher,_Kofiau_Paradise- Tanysiptera ellioti
Description: The Kofiau paradise-kingfisher has dark blue upperparts and a light blue crown. It has white underparts, rump, and tail. The bill is red. It is 33 to 34 cm long, including the tail.
Range: Indonesian island of Kofiau.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: The Kofiau paradise-kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of its restricted range.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_Keulemans 2) HectonichusRange: Indonesian island of Kofiau.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: The Kofiau paradise-kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of its restricted range.
2) Specimen
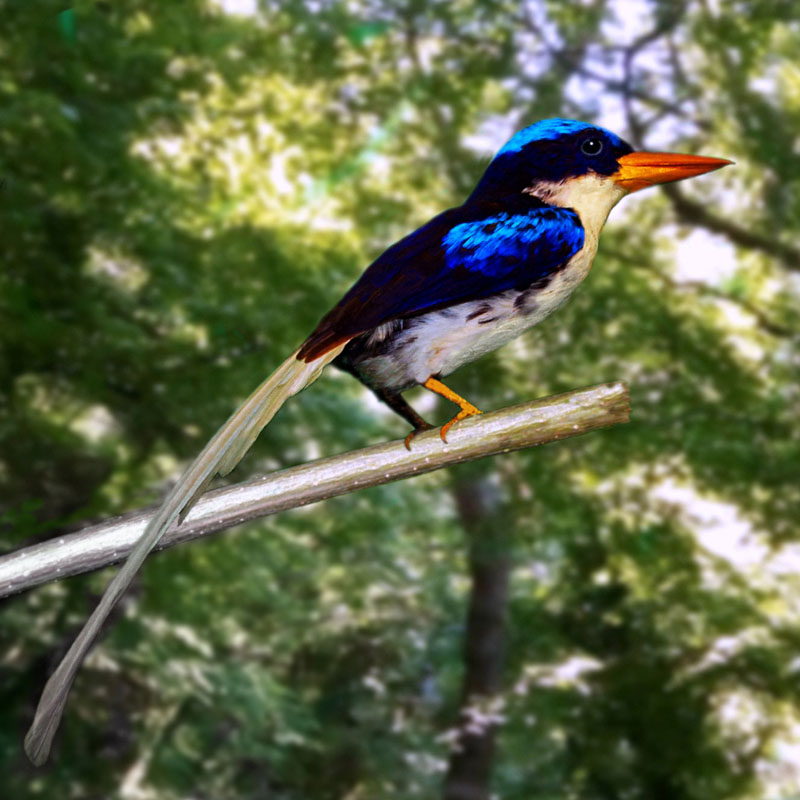


Kingfisher,_Little_Paradise- Tanysiptera hydrocharis
Description: The little paradise-kingfisher has dark blue upperparts including the crown. Its underparts and rump are white; the bill is red. The long blue tail has white edges. It is 31 inches long including the tail streamers.
Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Lowland forest, even some drier ones.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: It is listed as Data Defiicient which indicates that the population status is unknown.
Image by:
1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) John Gerrard Keulemans Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Lowland forest, even some drier ones.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: It is listed as Data Defiicient which indicates that the population status is unknown.
2) Adult and juvenile
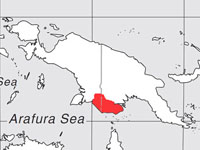

Kingfisher,_Numfor_Paradise- Tanysiptera carolinae
Description: The Numfor paradise-kingfisher has purplish-blue upperparts and underparts. The tail, lower back, and rump are white. The bill is red. This species is a result of some biak paradise-kingfishers arriving on Numfor and then slowly evolving.
Range: Indonesian island of Numfor northwestern of New Guinea.
Habitat: They have adapted to much of the island.
Diet: Grasshoppers, beetles, snails.
Conservation status:The Numfor paradise-kingfisher is listed as Near Threated because of its restricted range and also because of logging of their habitat.
Image by: 1) Von_RosenberRange: Indonesian island of Numfor northwestern of New Guinea.
Habitat: They have adapted to much of the island.
Diet: Grasshoppers, beetles, snails.
Conservation status:The Numfor paradise-kingfisher is listed as Near Threated because of its restricted range and also because of logging of their habitat.
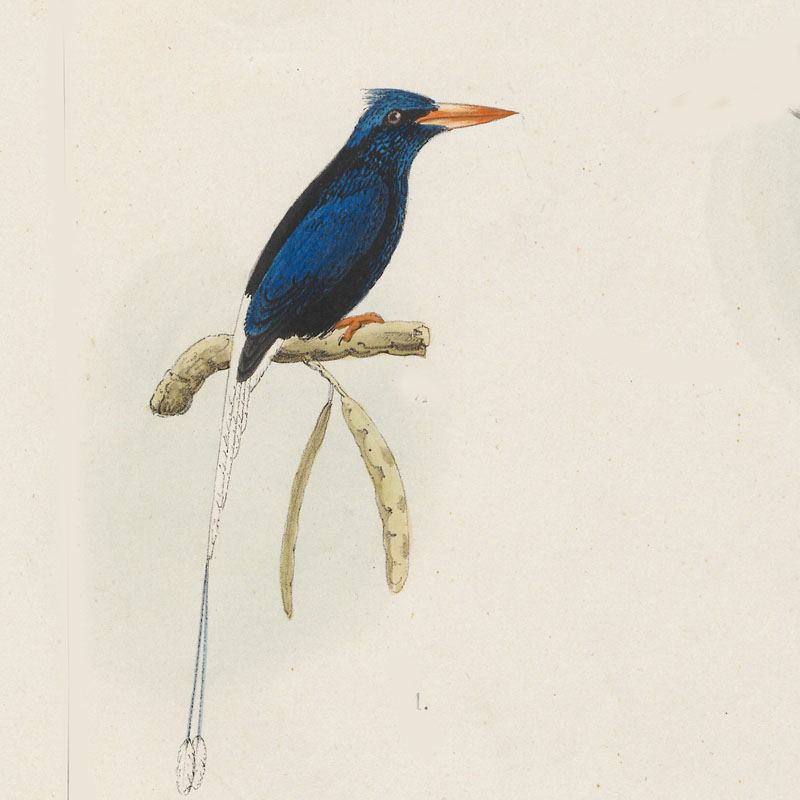

Kingfisher,_Red-breasted Tanysiptera nympha
Description: The red-breasted kingfisher has blue-black upperparts including the crown. It has a pink-red rump and underparts The bill and legs are orange-red. It has a blue tail with elongated central feathers which often have some white on them. It is 30 to 35 cm long which includes the tail-streamers.
Range: New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) John Gerrard KeulemansRange: New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forests, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
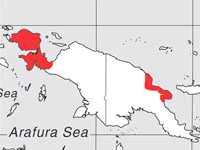

Genus Todiramphus
Members of Todiramphus are medium-sized kingfishers with flattened beaks. They are typically blue or blue-green above with pale underparts. They often have a pale collar and stripe over the eye. Most are found in Australasia. Many species are restricted to relatively small islands such as Guam and lesser known islands in French Polynesia. The conservation status of these more isolated species often indicates a threat to their population because of a small range and also due to deforestation. For these small isolated populations it can be difficult to observe and photograph them.
Many species are commonly found well away from water and feed largely on terrestrial animals such as insects and lizards. Ones that are found near water mainly eat crustaceans, snails, and small fish. As is true for all kingfishers, the nest is built in a cavity. Most often this is in a termite mound that is located in a tree. Sometimes termite mounds on the ground are used and sometimes tunnels are excavated in bankings. Tree cavities are also used.
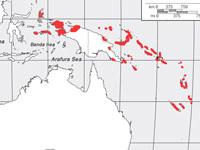
Kingfisher,_Beach Todiramphus saurophagus
Description: The beach kingfisher has greyish-blue upperparts, and a white head with a dark half eye-line. It has white underparts including the neck. The bill is dark with a lighter base of the lower mandible. It has black legs. It is 30 cm in length and weighs 90 to 145 grams. It has its nest in a tree cavity.
Range: New Guinea, Soloman Islands.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical mangrove forests.
Diet: Fish, crabs, insects. Dives for fish, seizes insects in trees or on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) Greg Miles - Papua New Guinea 3) Francesco_VeronesiRange: New Guinea, Soloman Islands.
Habitat: Subtropical or tropical mangrove forests.
Diet: Fish, crabs, insects. Dives for fish, seizes insects in trees or on the ground.
Conservation status: Least Concern.


Kingfisher,_Blue-and-white Todiramphus diops
Description: The blue-and-white kingfisher has blue upperparts including the head. It has a white loral spot, collar, and underparts. The female has a blue breast-band and lacks the white collar.They have a black bill and feet. It is 19 cm long.
Range: North Maluku in Indonesia.
Habitat: Woodlands, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, especially grasshoppers.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by:
1) Paulo Alves 2) Francesco_Veronesi 3) Kingfisher,_Blue-and-white_Francesco_VeronesiRange: North Maluku in Indonesia.
Habitat: Woodlands, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, especially grasshoppers.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1) Female on left 2) Female 3) Male
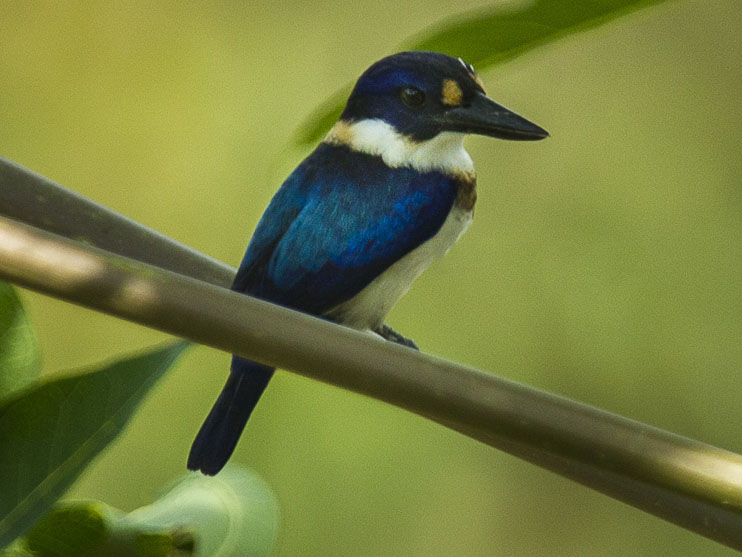



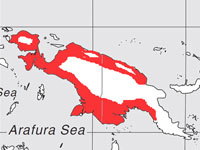
kingfisher,_Blue-black Todiramphus nigrocyaneus
Description: The blue-black kingfisher has black-and-blue upperparts, blue crown, blue breast band, and a white throat. It has a black bill and greyish-black legs.The female has a white lower-breast and belly while the male has mostly blue underparts with a white breast spot. It is 23 cm long and weighs about 55 grams with the female heavier than the male.
Range: New Guinea and nearby islands.
Habitat: Forests near water.
Diet: Fish, crabs, lizards.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of lack of data, but also a suspicion that the population is declining.
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) Joseph_WolfRange: New Guinea and nearby islands.
Habitat: Forests near water.
Diet: Fish, crabs, lizards.
Conservation status: It is listed as Near Threatened because of lack of data, but also a suspicion that the population is declining.

Kingfisher,_Chattering Todiramphus tutus
Description: The chattering kingfisher has a blue-green back and crown. It has a blackish eye-line that encircles the head with a white encircling streak above and also a white collar below. The throat and underparts are white. It can be told from the Society kingfisher by the complete white collar. It is 22 cm in length.
Range: Cook Islands and Society Islands of French Polynesia.
Habitat: Moist primary or secondary forests. Also old plantations.
Diet: Insects including grasshoppers and termites. Also worms, shrimp, fish. Takes prey on foliage, in flight, or from shallow water.
Conservation status: The chattering kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of its restricted range, increasing human population and habitat degradation.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_KeulemansRange: Cook Islands and Society Islands of French Polynesia.
Habitat: Moist primary or secondary forests. Also old plantations.
Diet: Insects including grasshoppers and termites. Also worms, shrimp, fish. Takes prey on foliage, in flight, or from shallow water.
Conservation status: The chattering kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of its restricted range, increasing human population and habitat degradation.
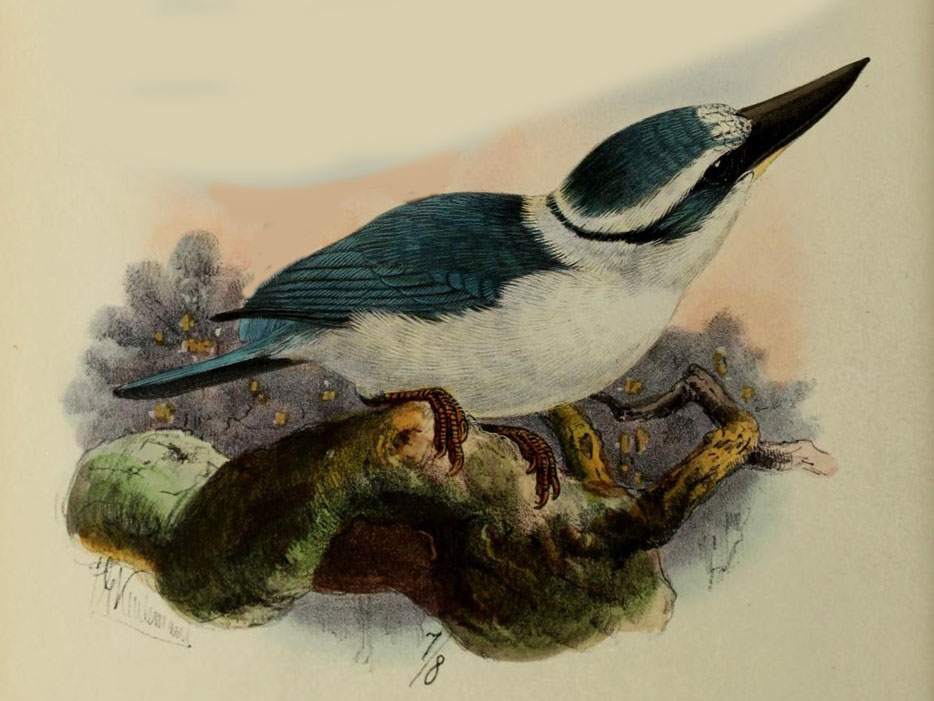

Kingfisher,_Chestnut-bellied Todiramphus farquhari
Description: The chestnut-bellied kingfisher, also known as the Vanuatu kingfisher, has dark blue upperparts including the tail. It has a white throat, collar, and lores. The underparts are orange, except the female has a white lower belly. It is 21 cm long and weights about 40 grams. It nests in trees in a termite mound or a cavity.
Range: Vanuatu which is 1800 km northeast of Australia.
Habitat: Prefers lowland primary forests; also farmland.
Diet: Insects, spiders, lizards. Catches prey in the air, on foliage, or on the ground.
Conservation status: The chestnut-bellied kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss and degradation.
Image by: 1) John Gerrard KeulemansRange: Vanuatu which is 1800 km northeast of Australia.
Habitat: Prefers lowland primary forests; also farmland.
Diet: Insects, spiders, lizards. Catches prey in the air, on foliage, or on the ground.
Conservation status: The chestnut-bellied kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss and degradation.

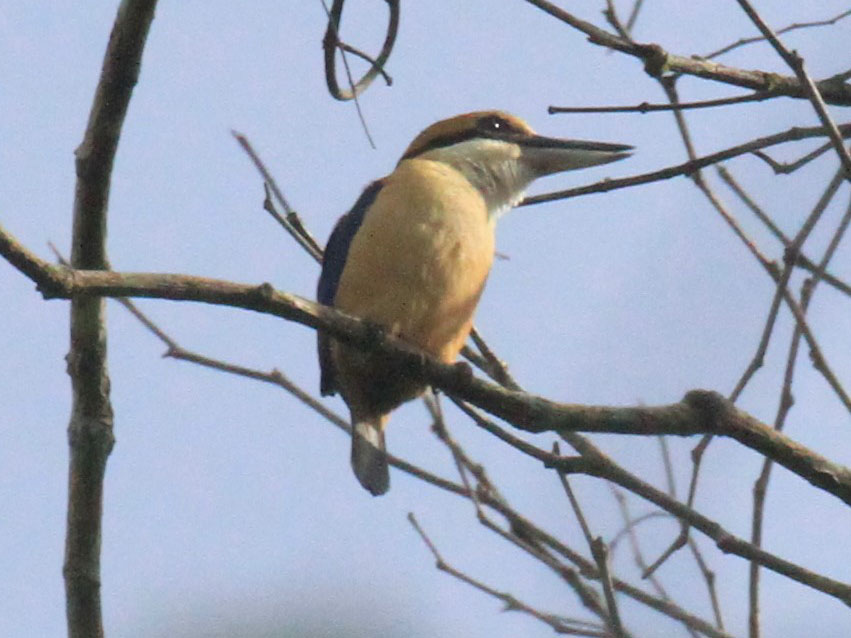
Kingfisher,_Cinnamon-banded Todiramphus australasia
Description: The cinnamon-banded kingfisher has dark green upperparts including the crown. The wings, rump, and tail are blue. It has a black mask. The underparts, lores, eyebrow, and collar are rufous. The upper-bill is black and the lower is yellowish. The legs are blackish. It is 21 cm long and averages 45 grams.
Range: Indonesia, East Timor.
Habitat: Wooded areas. Prefers a closed canopy.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: The cinnamon-banded kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss and degradation.
Image by: 1) Ron Knight 2) Charles_Davies - Tanimbar Islands of Indonesia, Range: Indonesia, East Timor.
Habitat: Wooded areas. Prefers a closed canopy.
Diet: Insects, larvae.
Conservation status: The cinnamon-banded kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened due to habitat loss and degradation.


Kingfisher,_Collared Todiramphus chloris Found: Asia, Australasia
Description: The collared kingfisher has upperparts that vary from blue to green and underparts that vary from white to buff. It has a white collar, white loral spot, and sometimes has a black eye-line. The bill is black with a pale yellow base to the lower mandible. Females tend to be greener than males. It is 24 cm long. It nests mainly in trees in a termite mound or tree cavity. It will also nest in an earth banking.
Range: From the Red Sea, across southern Asia, to Polynesia.
Habitat: Coastal areas, especially mangroves.
Diet: Mainly crab and shrimp. Also insects, worms, snails, reptiles, fish.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Balaji Venkatesh_Sivaramakrishnan 2) Johnny Wee 3) JJ
Harrison - Thailand 4) Dick Daniels - Miami Zoo Range: From the Red Sea, across southern Asia, to Polynesia.
Habitat: Coastal areas, especially mangroves.
Diet: Mainly crab and shrimp. Also insects, worms, snails, reptiles, fish.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1) Female




Kingfisher,_Flat-billed Todiramphus recurvirostris
Description: The flat-billed kingfisher is similar to the collared kingfisher, but has cinnamon flanks. Its bill is also flatter and shorter than the collared kingfisher.
Range: Samoa.
Habitat: Not found in highlands.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_KeulemansRange: Samoa.
Habitat: Not found in highlands.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Least Concern.

Kingfisher,_Forest Todiramphus macleayii
Description: The forest kingfisher is predominantly blue and white. It has white lores, a broad black eye-stripe, and a black bill with a pale lower base. The legs are blackish. It is 20 cm in length and weighs about 38 grams. The nest is usually excavated with helpers in an arboreal termite mound. Natural tree cavities are also used. The similar collared kingfisher usually has some greenish upperparts,
Range: New Guinea, Australia, Solomon Islands.
Habitat: Forests, mangroves, and swamps.
Diet: Insects such as beetles and grasshoppers, worms, fish, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) David Cook - Queenslanda 2) JJ Harrison - Queensland 3) Geoff_Whalan - Northern Territory, AU 4) Frank
Wouters Range: New Guinea, Australia, Solomon Islands.
Habitat: Forests, mangroves, and swamps.
Diet: Insects such as beetles and grasshoppers, worms, fish, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
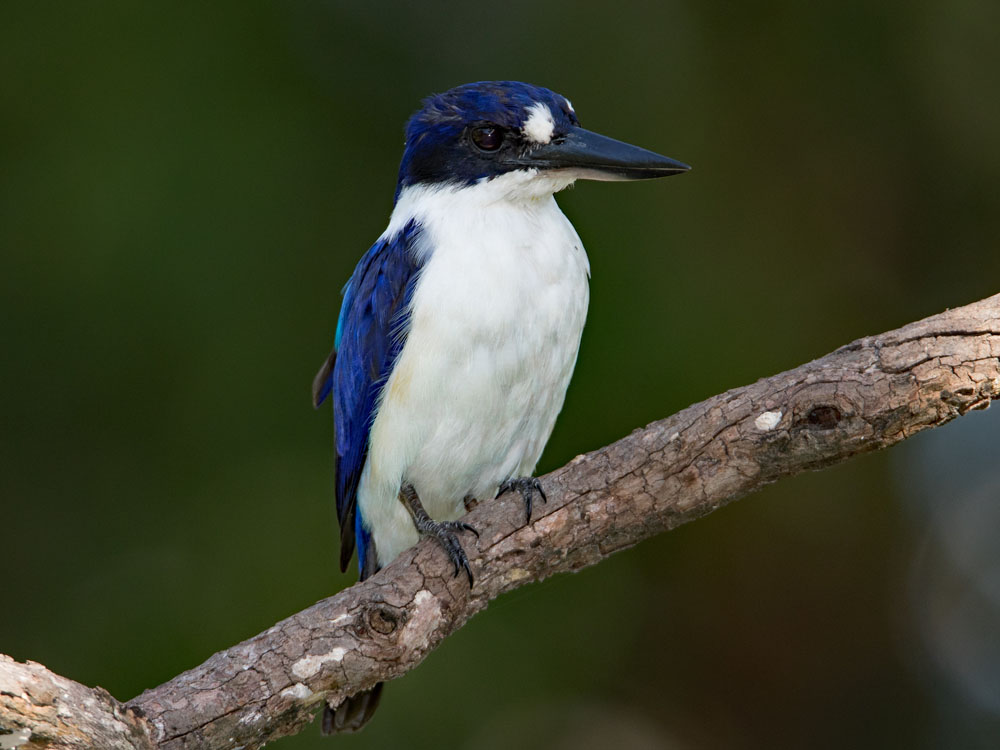




Kingfisher,_Guam Todiramphus cinnamominus Found: Guam
Description: The Guam kingfisher has blue upperparts and a rusty-cinnamon head. The male has cinnamon underparts and the female has white underparts. It nests in tree cavities and arboreal termite nests. It is 20 to 24 cm long.
Range: Initially Guam, now captive breeding programs.
Habitat: Were found in various types of forest.
Diet: Insects, geckos. In captivity it will also eat mice and worms.
Conservation status: It is restricted to a captive breeding program following its extinction in the wild due to the introduced brown tree snake.
Image by: 1) Kevin 2) Fred_Faulkner - Lincoln Park Zoo 3) Eric_Savage 4) Dick Daniels - San Diego ZooRange: Initially Guam, now captive breeding programs.
Habitat: Were found in various types of forest.
Diet: Insects, geckos. In captivity it will also eat mice and worms.
Conservation status: It is restricted to a captive breeding program following its extinction in the wild due to the introduced brown tree snake.
1, 2) Female 3, 4) Male
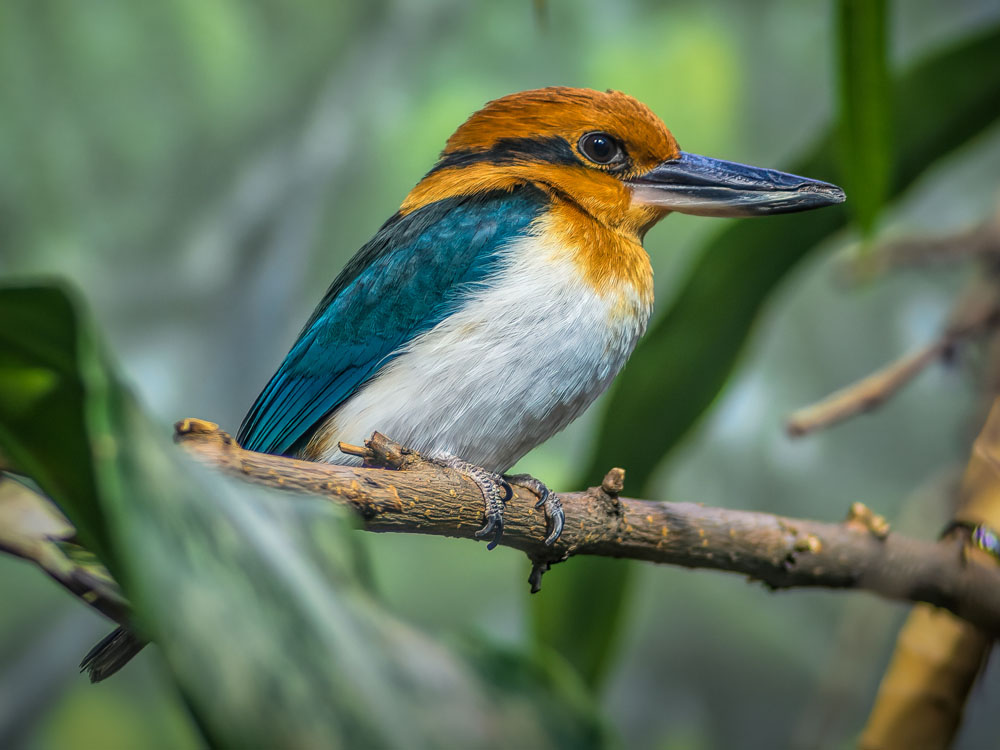




Kingfisher,_Lazuli Todiramphus lazuli
The lazuli kingfisher has mainly blue and turquoise plumage. It has a white throat and white lores. The male has a pale blue breast and a white belly. The female has a pale blue breast and belly. They are 22 cm long. The name refers to the color of the semi-precious stone Lapis lazuli.
Description:
Range: Southern Maluku Islands in Indonesia.
Habitat: Land with some trees, but probably avoids primary forests.
Diet: Grasshoppers and beetles.
Conservation status: The lazuli kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of hunting.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_Keulemans Description:
Range: Southern Maluku Islands in Indonesia.
Habitat: Land with some trees, but probably avoids primary forests.
Diet: Grasshoppers and beetles.
Conservation status: The lazuli kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of hunting.
1) Female on left, male right

Kingfisher,_Mangareva Todiramphus gambieri Found: French Polynesia
Description: The Mangareva kingfisher has mainly blue or green-blue upperparts. It has a cream colored head and neck, plus a white chin, The crown has a variable abount of blue. There is a bluish line to the rear of eye. The Mangareva kingfisher and Niau kingfisher were formerly considered a subspecies of the Tuamotu kingfisher.
Range: Island of Niau in the Tuamotus of French Polynesia.
Habitat: Semi-open area with some trees.
Diet: Insects and small lizards.
Conservation status: The Mangareva kingfisheris listed as Critically Endangered with a population of under 200. They have suffered from cats eating chicks and food competition with rats.
No image available.Range: Island of Niau in the Tuamotus of French Polynesia.
Habitat: Semi-open area with some trees.
Diet: Insects and small lizards.
Conservation status: The Mangareva kingfisheris listed as Critically Endangered with a population of under 200. They have suffered from cats eating chicks and food competition with rats.
Kingfisher,_Mariana Todiramphus albicilla
Description: The Mariana kingfisher has a green crown and back, a black eye-line, blue-green wings and tail. The underparts are white. The bill is black with some yellow on the base. It
was formerly considered a subspecies of the Collared kingfisher.
Range: Mariana Islands (northeast of Philippines).
Habitat: A generalist, but prefers coastal regions.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Not rated.
Image by: 1) PeterRange: Mariana Islands (northeast of Philippines).
Habitat: A generalist, but prefers coastal regions.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Not rated.

Kingfisher,_Marquesas Todiramphus godeffroyi
Description: The Marquesas kingfisher has a white mantle. It has a blue lower back, rump, tail and wings. The white head has a dark line behind eye. The underparts are white. It has a black upper-bill and pale yellow lower-bill. The length is 21 cm.
Range: Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia .
Habitat: Prefers dense humid forests. Also found in coconut plantations.
Diet: Mainly grasshoppers and beetles. Also lizards.
Conservation status: The Marquesas kingfisher is listed as Critically Endangered because there are fewer than 500 left in the wild.
No image available.Range: Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia .
Habitat: Prefers dense humid forests. Also found in coconut plantations.
Diet: Mainly grasshoppers and beetles. Also lizards.
Conservation status: The Marquesas kingfisher is listed as Critically Endangered because there are fewer than 500 left in the wild.
Kingfisher,_Melanesian Todiramphus tristrami
Description: The Melanesian kingfisher has blue to green upperparts, plus white or buff underparts and collar. I has a wide black eye-line.
Range: Bismarck Archipelago and Solomon Islands which are northeast of New Guinea.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests and plantations.
Diet: Insects if inland; crustaceans and small fish if coastal.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_Keulemans 2) Nik_Borrow.Range: Bismarck Archipelago and Solomon Islands which are northeast of New Guinea.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests and plantations.
Diet: Insects if inland; crustaceans and small fish if coastal.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
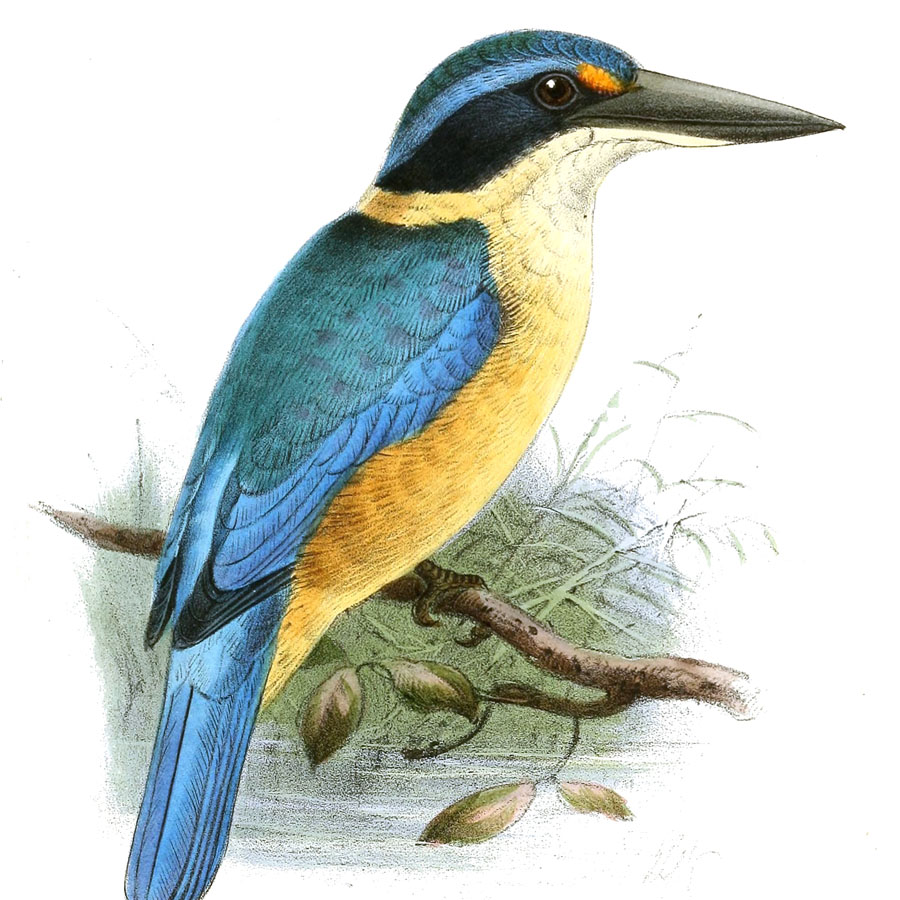

Kingfisher,_Mewing Todiramphus ruficollaris
Description: The mewing kingfisher, also known as the Mangaia kingfisher, has blue-green upperparts and cap. It has a yellow-orange collar, white underparts, and black bill with pale base to the lower-bill. The legs are blackish. It is 22 cm in length.
Range: Mangaia in the Cook Islands.
Habitat: Forests, preferring unbroken canopy.
Diet: Termites, grasshoppers, caterpillars, worms, lizards.
Conservation status: It is listed as Vulnerable due to habitat loss and by disturbance by the introduced common mynas.
No available imagesRange: Mangaia in the Cook Islands.
Habitat: Forests, preferring unbroken canopy.
Diet: Termites, grasshoppers, caterpillars, worms, lizards.
Conservation status: It is listed as Vulnerable due to habitat loss and by disturbance by the introduced common mynas.
Kingfisher,_New_Britain Todiramphus albonotatus
Description: The New Britain kingfisher, also known as the white-mantled kingfisher, has blue wings and tail. It has a turquoise crown, thick black eye-line, white collar, white underparts, and black bill. The female is similar to the male but has blue on the lower back. It is 16 to 18 cm long.
Range: New Britain off New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary forests; also forest edges, forest clearings, and logged forests.
Diet: Insects.
Conservation status: The New Britain kingfisher is listed as Near Treatened because of its restricted range and habitat degradation.
Image by: 1) Katerina_Tvardikova 2) David_Cook 3) Nik_BorrowRange: New Britain off New Guinea.
Habitat: Primary forests; also forest edges, forest clearings, and logged forests.
Diet: Insects.
Conservation status: The New Britain kingfisher is listed as Near Treatened because of its restricted range and habitat degradation.


Kingfisher,_Niau Todiramphus gertrudae Found:French Polynesia
Description: The Niau kingfisher has a green back, blue wings, a dusty orange head, and white underparts. There is a bluish line to the rear of the eye. The Mangareva kingfisher and Niau kingfisher were formerly considered a subspecies of the Tuamotu kingfisher.
Range: Island of Niau in the Tuamotus, French Polynesia.
Habitat: Coconut plantations, village gardens.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Niau kingfisher is listed as Critically Endangered. There are only approximately 100 left.
Images unavailable.Range: Island of Niau in the Tuamotus, French Polynesia.
Habitat: Coconut plantations, village gardens.
Diet: Unknown.
Conservation status: Niau kingfisher is listed as Critically Endangered. There are only approximately 100 left.
Kingfisher,_Pacific Todiramphus sacer :
Description: The Pacific kingfisher has various plumages. The male Pacific kingfisher of the nominate race has a greenish-blue crown and upperparts, brighter rump, plus blue wings and tail. It has a wide black mask that narrows and continues around the head. The underparts are white. The female is duller.
The Pacific kingfisher was previously considered a subspecies of the Collared kingfisher. It is 23 to 25 cm long.
Range: South Pacific Islands such as Fiji, Tonga, and American Samoa.
Habitat: Mangroves, cultivated land.
Diet: Coastal birds favor crustaceans, inland favor insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Tom Tarrant - Fiji 2) Mikes_Birds - FijiRange: South Pacific Islands such as Fiji, Tonga, and American Samoa.
Habitat: Mangroves, cultivated land.
Diet: Coastal birds favor crustaceans, inland favor insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
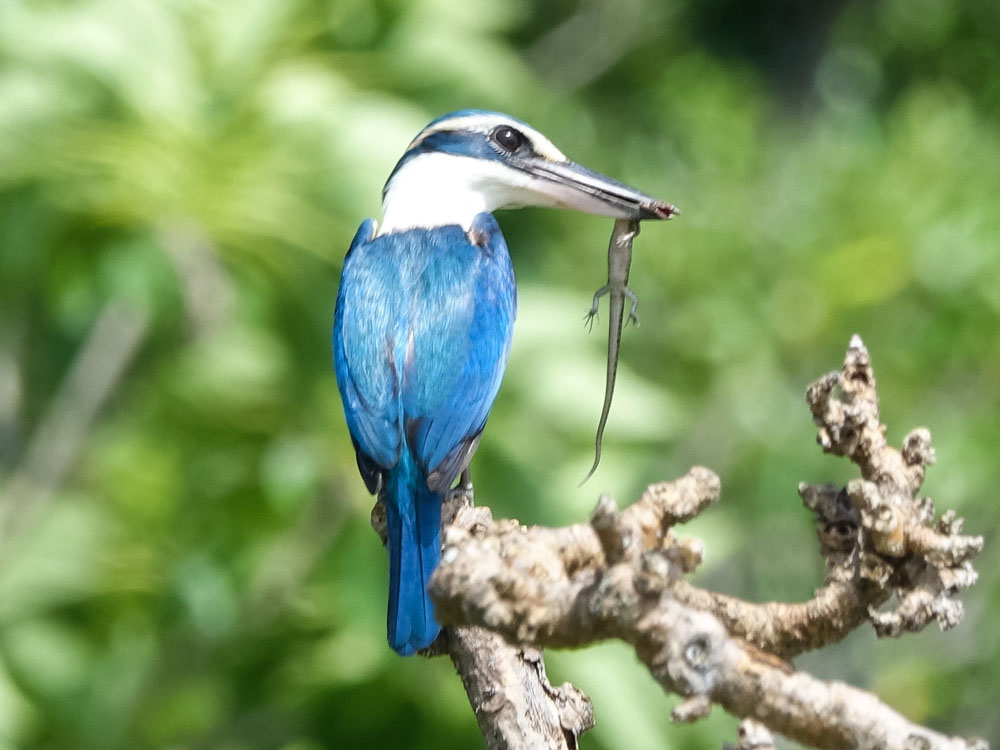


Kingfisher,_Palau Todiramphus pelewensis
Description: The Palau kingfisher, also known as the rusty-capped kingfisher, has blue-green upperparts, bluer wings, orange-rufous cap, black eye-line that continues around the nape, and white underparts. It has a black upper-bill, ivory and black lower-bill. It is a small kingfisher with a length of 20 cm. The Palau kingfisher
was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the Micronesian kingfisher.
Range: Palau in Micronesia
Habitat: Moist lowland forests.
Diet: Insects, geckos.
Conservation status: The Palau kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of its small range. However, its population does seem to be stable.
Image by: 1) thibaudaronsonRange: Palau in Micronesia
Habitat: Moist lowland forests.
Diet: Insects, geckos.
Conservation status: The Palau kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of its small range. However, its population does seem to be stable.

Kingfisher,_Pohnpei Todiramphus reichenbachii
Description: The Pohnpei kingfisher has blue-green upperparts, rufous cap, black eye-line that continues around to the nape, and white underparts. It has a black upper-bill, ivory and black lower-bill. The female has some rufous on its breast. It is a small kingfisher with a length of 20 cm. It
was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the Micronesian kingfisher.
Range: Pohnpei of Micornesia
Habitat: Moist lowland forests.
Diet: Insects, geckos.
Conservation status: The Pohnpei kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of its small range. However, its population does seem to be stable. There is a worry that the brown-tree snake could become invasive.
Image by: 1) Dylan_Kesler 2) thibaudaronsonRange: Pohnpei of Micornesia
Habitat: Moist lowland forests.
Diet: Insects, geckos.
Conservation status: The Pohnpei kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of its small range. However, its population does seem to be stable. There is a worry that the brown-tree snake could become invasive.


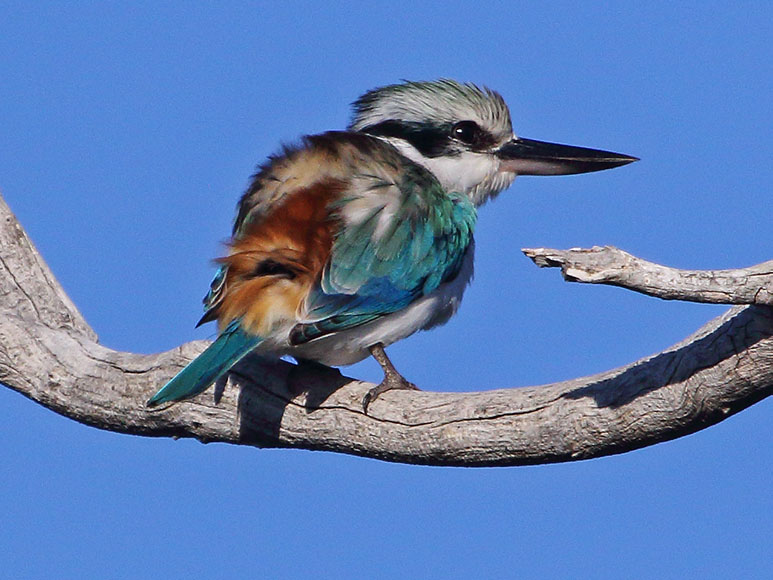
Kingfisher,_Red-Backed Todiramphus pyrrhopygius
Description: The red-backed kingfisher has a streaked green and white crown. The wings and tail are bluish-green. It has a red rump and upper tail coverts. The nape and underparts are white. There is a black band from the base of bill, through eyes, and beyond to the nape. The upper-bill is black, the lower-bill is pale, and the legs are dark grey. It is 22 cm long and weighs about 55 grams. The nest is excavated by the pair, usually in a banking; also in aerial or ground termite nests.
Range: Australia.
Habitat: Dry areas with open woodlands, grasslands with some trees.
Diet: Mainly insects; also spiders, centipedes, fish, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Richard Fisher 2) David_Cook - South Australia 3) Brian_McCauleyRange: Australia.
Habitat: Dry areas with open woodlands, grasslands with some trees.
Diet: Mainly insects; also spiders, centipedes, fish, frogs.
Conservation status: Least Concern.



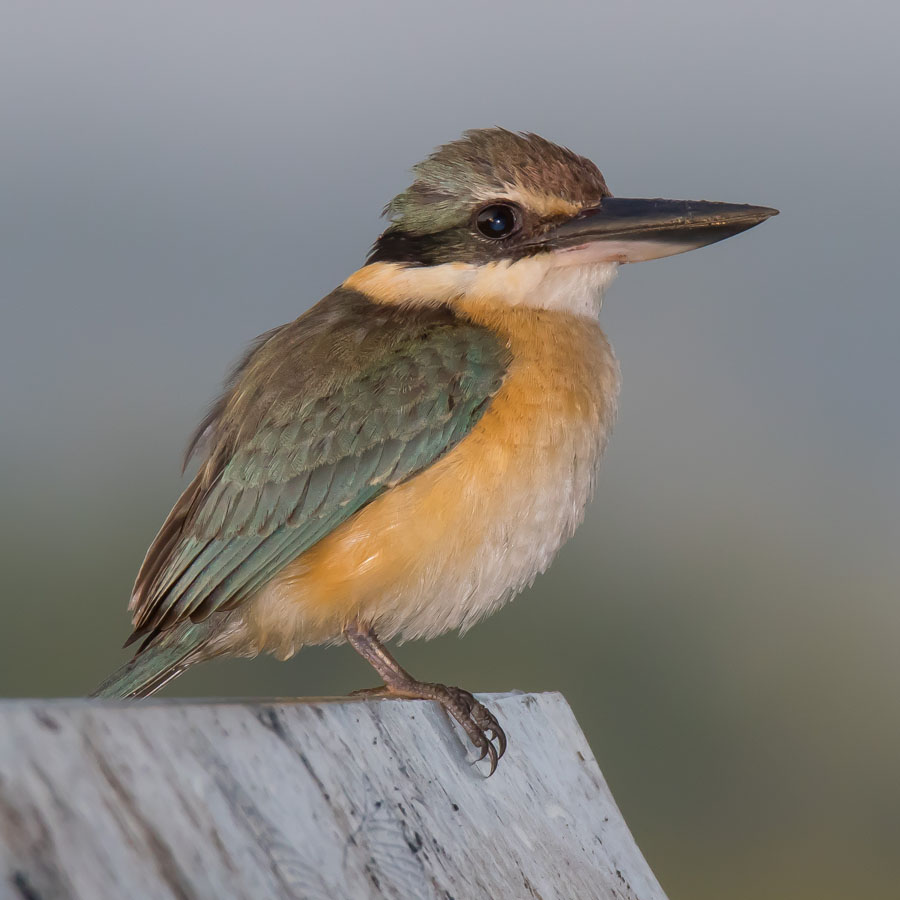
Kingfisher,_Sacred Todiramphus sanctus
Description: The Sacred kingfisher has turquoise upperparts and head. It has a black mask and buff lores. The throat and neck are white. It has yellowish-buff underparts. The upper-bill is black, the lower-bill is ivory with a black tip. The female has greener upperparts than the male. It is 20 to 23 cm long. It nests in tree hollows, tunnels they excavate, and arboreal termite mounds.
Range: Australia, Newe Guinea, New Zealand.
Habitat: Open woodlands, grasslands with trees, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, spiders, crustaceans; also fish, frogs, reptiles.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Geoff_Whalan - Northern Territory 2) Leo - New South Wales 3, 4) birdsaspoetry Range: Australia, Newe Guinea, New Zealand.
Habitat: Open woodlands, grasslands with trees, mangroves.
Diet: Insects, spiders, crustaceans; also fish, frogs, reptiles.
Conservation status: Least Concern.




Kingfisher,_Society Todiramphus veneratus
Description: The male Society kingfisher, also known as the Tahiti kingfisher, has brown or blue-green upperparts depending on the subspecies. The underparts are white. The female has brown upperparts, a brown breast-band, and the rest of the underparts are white.
Range: French Polynesia.
Habitat: Moist forests.
Diet: Insects, larvae, fish, crustaceans. Prey captured in flight, on the ground, or via dives into shallow water.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) John _Gerrard_Keulemans 2) Erica SpotswoodRange: French Polynesia.
Habitat: Moist forests.
Diet: Insects, larvae, fish, crustaceans. Prey captured in flight, on the ground, or via dives into shallow water.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
1) Female on left; 2 male subspecies on right
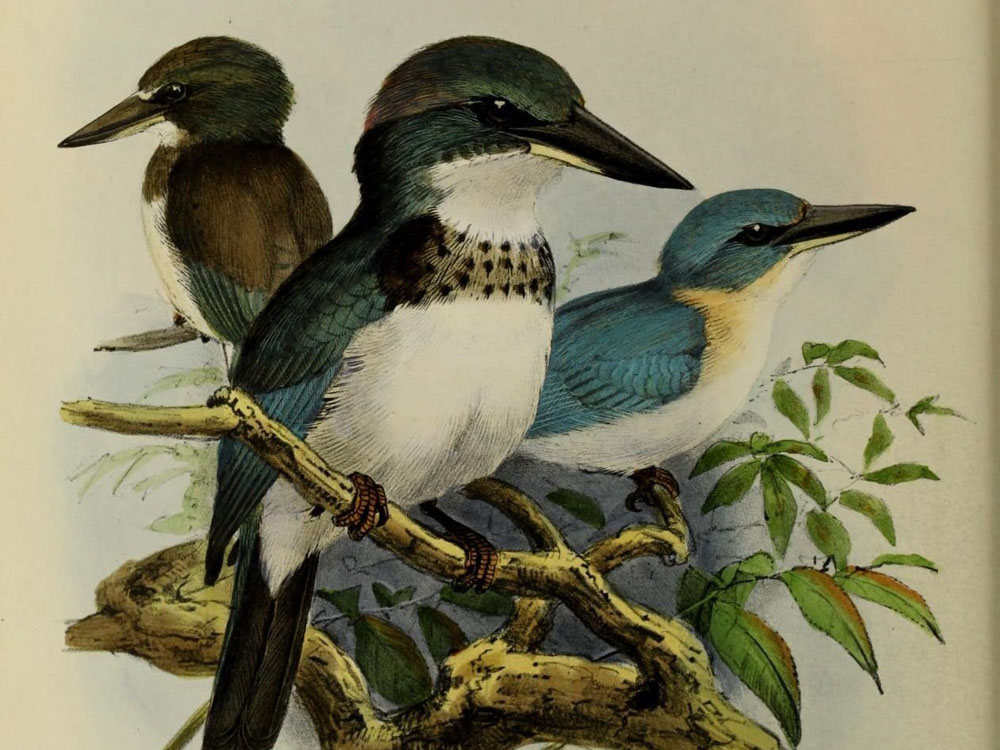

Kingfisher,_Sombre Todiramphus funebris Found: Halmahera (Indonesian island)
Description: The sombre kingfisher has dark upperparts, and a partial dark collar. The head is also sombre with a white supercilium that continues to the nape, and a white loral spot. It has white underparts and a white collar. It is a large kingfisher with a length of 30 cm. The bill is black with a ivory lower-bill base.
Range: Island of Halmahera, in North Maluku, Indonesia.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forest, mangroves.
Diet: Insects such as grasshoppers, centipedes, snakes, lizards.
Conservation status: The sombre kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of a relatively small population and ongoing logging.
Image by:
1) Paulo Alvres 2) Pete_Morris Francesco_Veronesi 3) Bill_BaconRange: Island of Halmahera, in North Maluku, Indonesia.
Habitat: Primary and secondary forest, mangroves.
Diet: Insects such as grasshoppers, centipedes, snakes, lizards.
Conservation status: The sombre kingfisher is listed as Vulnerable because of a relatively small population and ongoing logging.
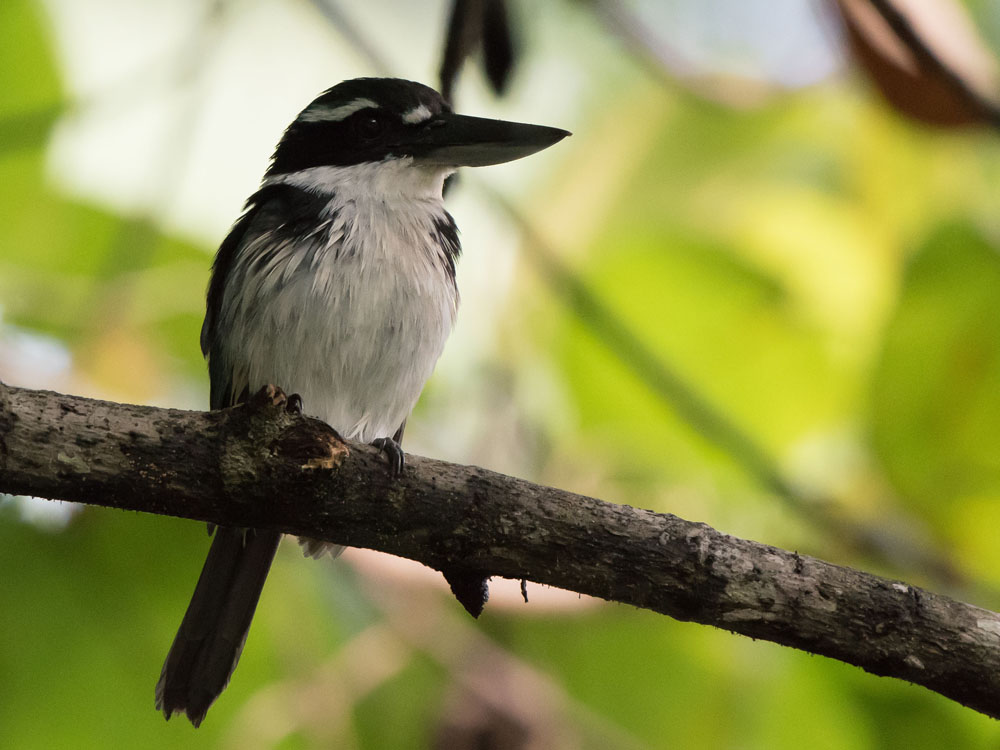



Kingfisher,_Talaud Todiramphus enigma Found: Indonesia
Description: The Talaud kingfisher has dark green upperparts, dark bluish-green crown, black mask, and green-blue wings plus tail. It has white underparts, loral spot, and collar. It has a black bill with a yellowish base to the lower-bill. The Talaud kingfisher is 21 inches in length.
Range: Talaud Islands north of Sulawesi in Indonesia.
Habitat: Forests and forest edgers, especially near water.
Diet: Insects, especially grasshopper. Also snails.
Conservation status: The Talaud kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of habitat loss due to logging.
Image by: 1)AriefrahmanRange: Talaud Islands north of Sulawesi in Indonesia.
Habitat: Forests and forest edgers, especially near water.
Diet: Insects, especially grasshopper. Also snails.
Conservation status: The Talaud kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of habitat loss due to logging.

Kingfisher,_Torresian Todiramphus sordidus
Description: The male Torresian kingfisher has greenish-blue upperparts and crown, a black mask, white collar, white lores, and white underparts. It has a black upper-bill and mostly ivory under-bill with a black tip. The female is slightly duller. Other subspecies are bluer. It is 23 to 25 cm long. It
was formerly consider a subspecies of the Collared kingfisher.
Range: Northern Australia, southern New Guinea.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests, mangroves, and plantations.
Diet: Coastal birds favor crustaceans, inland favor insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) Bird_Team 2) Wynnum - Queensland 3) JJ_Harrison - Darwin, AU Range: Northern Australia, southern New Guinea.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests, mangroves, and plantations.
Diet: Coastal birds favor crustaceans, inland favor insects.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
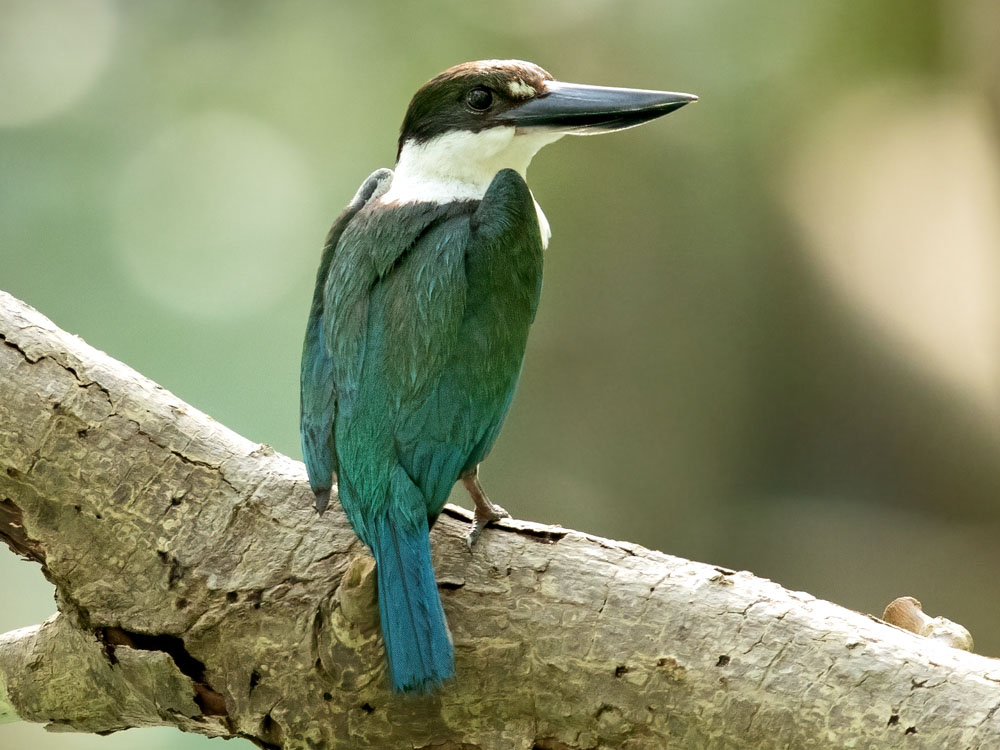



Kingfisher,_Ultramarine Todiramphus leucopygius
Description: The ultramarine kingfisher has dark blue upperparts including the head. It has a purple rump and tail; white underparts, collar, and throat. The male has a white lower-mantle while on the female it is dark blue. They are 21 cm long, weigh about 45 grams with the female slighjly larger.
Range: Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests, areas with scattered trees.
Diet: Insects and spiders.
Conservation status: Least Concern.
Image by: 1) John Gerrard Keulemans 2, 3) Tony_MorrisRange: Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands.
Habitat: Moist lowland forests, areas with scattered trees.
Diet: Insects and spiders.
Conservation status: Least Concern.



Kingfisher,_Vanuatu Todiramphus farquhari
Description: The Vanuatu kingfisher has dark blue upperparts and mainly a black head. It has white lores, throat, and collar. The underparts are bright orange. It measures 19–21 cm in length and weighs 32-42 grams. The pair usually excavates a tunnel in an arboreal termite mound. They will also use an existing cavity in a palm tree. The only other kingfisher in Vanuatu is the Pacific kingfisher which has paler blue-green upperparts, whiter underparts and a buff stripe above the eye.
Range: Vanuatu of French Polynesia
Habitat: Lowland dense forests.
Diet: Insects such as beetles. Also lizards and spiders.
Conservation status: The Vanuatu kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of deforestation.
Image by: 1) John_Gerrard_KeulemansRange: Vanuatu of French Polynesia
Habitat: Lowland dense forests.
Diet: Insects such as beetles. Also lizards and spiders.
Conservation status: The Vanuatu kingfisher is listed as Near Threatened because of deforestation.

